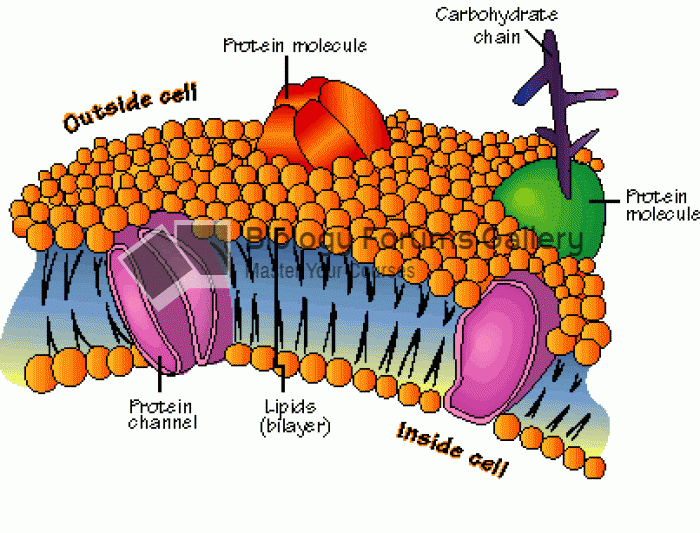
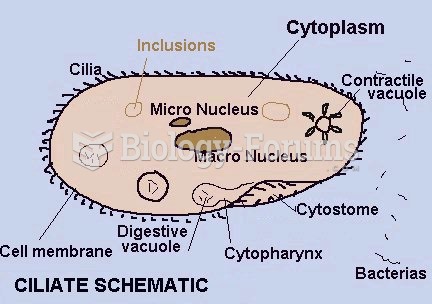
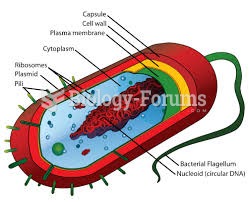
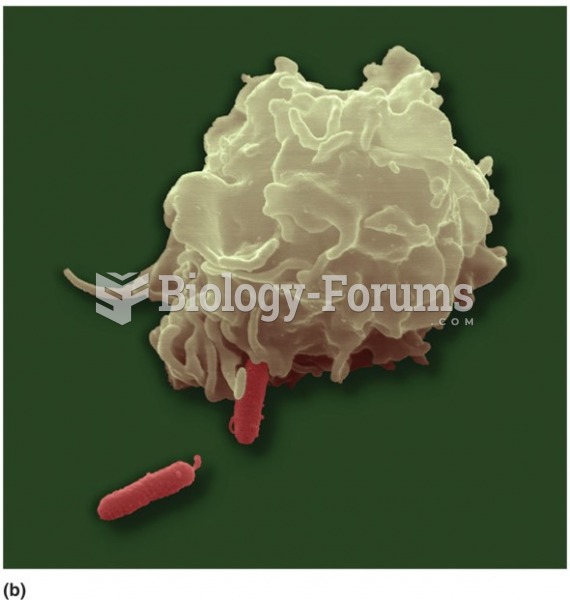
|
|
|
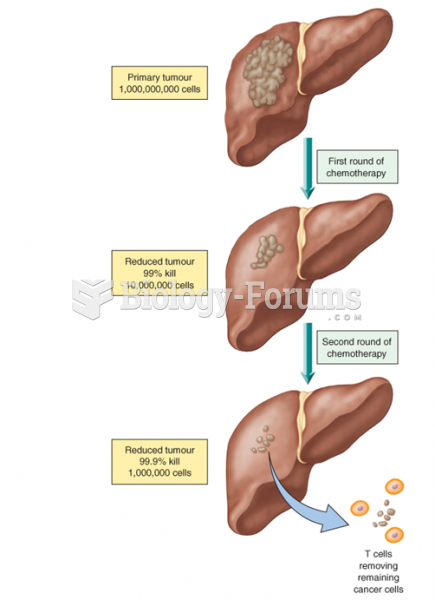
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.