This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Did you know?
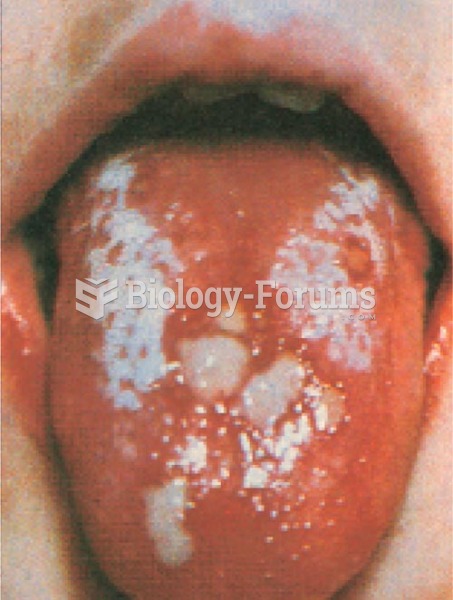
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.
Did you know?
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
Did you know?
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.