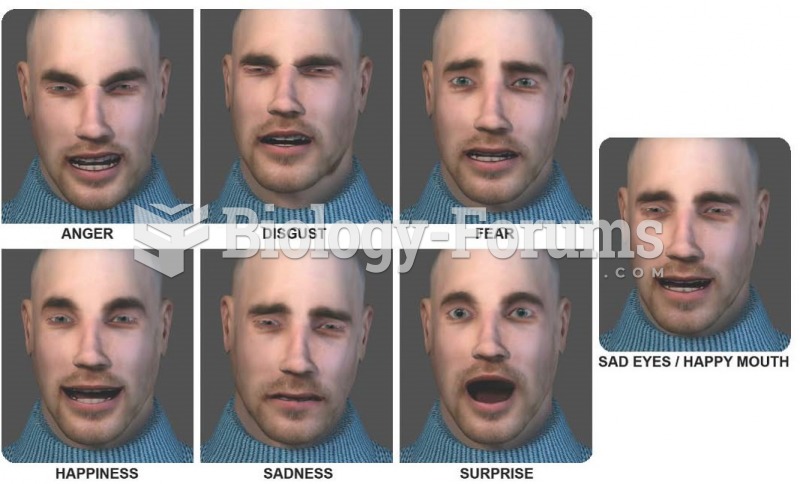
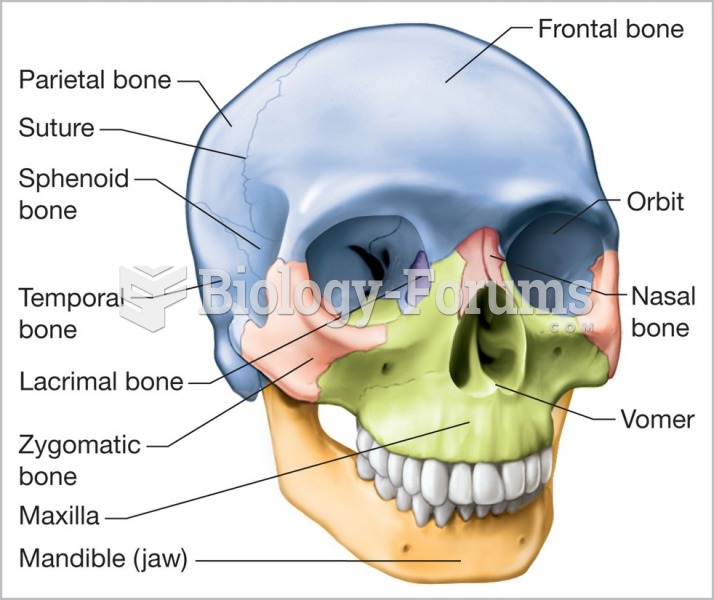
Answer to Question 1
Answer: Happiness is more easily decoded in the faces of women, and anger is more easily decoded in the faces of men. Knowing that her partner is angry would be a useful skill for a female. She would know better when to approach him for things she needs, to ask for assistance, and to initiate sexual activity. Also, for males, knowing when his partner is happy would assist him with knowing when his sexual advances might be welcome and when her and the children's needs were fulfilled. All of these would increase the chance of procreation and the survival of offspring, making the ability more likely to be passed along as well.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Kelley postulated that people use three kinds of information to decide whether the cause of an event is internal or external to the person. Consistency information is information about how a person reacts to a stimulus over time; consensus information is information about how other people react to the stimulus; and distinctiveness information is information about how a person reacts to other similar stimuli. When consistency, consensus, and distinctiveness are all high, people tend to make an external attribution to the stimulus. For example, presume that Nell, a student, falls asleep in class. If she falls asleep in class every session (high consistency), if other students also fall asleep in the class (high consensus), and if she does not fall asleep in her other classes (high distinctiveness), one would conclude that she falls asleep because the class is boring. If, however, consistency is high but consensus and distinctiveness are low (she always falls asleep, but no one else does and she falls asleep in all of her other classes), one would conclude that there's something about Nell that is making her fall asleep. Finally, when consistency is low (Nell only falls asleep once, or occasionally), a situational attribution is made: there must have been something about the particular situation (e.g., she pulled an all-nighter the previous evening) that led to her falling asleep.