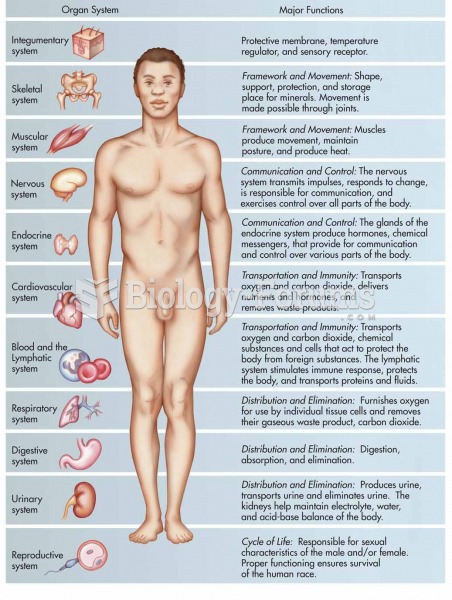
|
|
|
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Limit intake of red meat and dairy products made with whole milk. Choose skim milk, low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Limit fried food. Use healthy oils when cooking.
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.