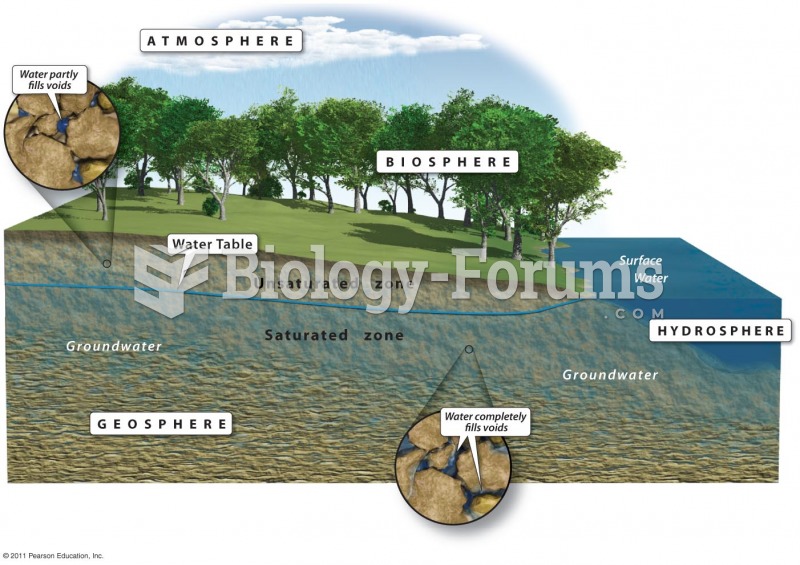
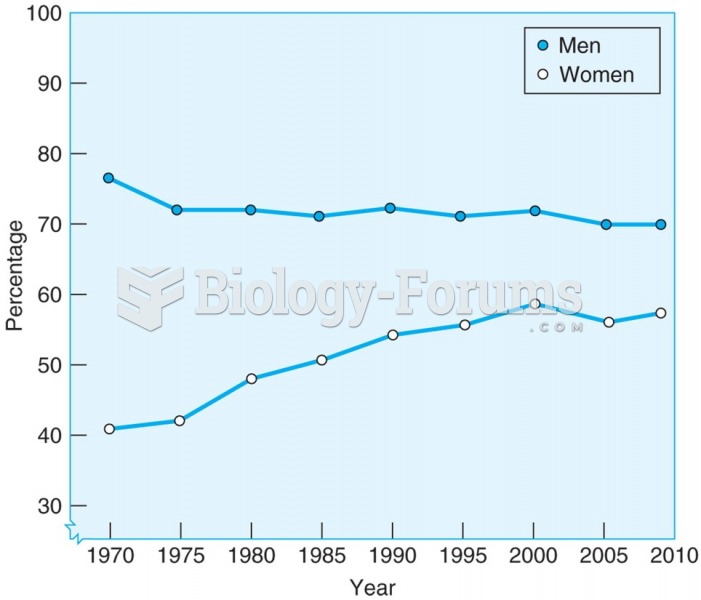
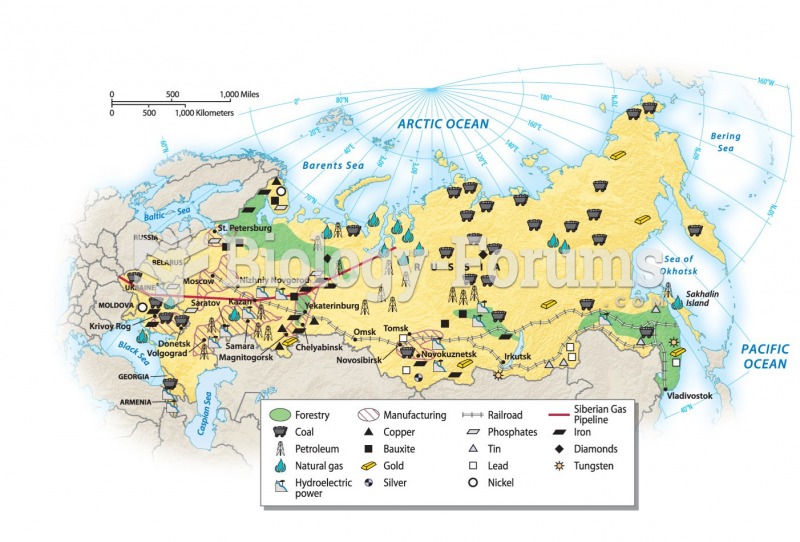
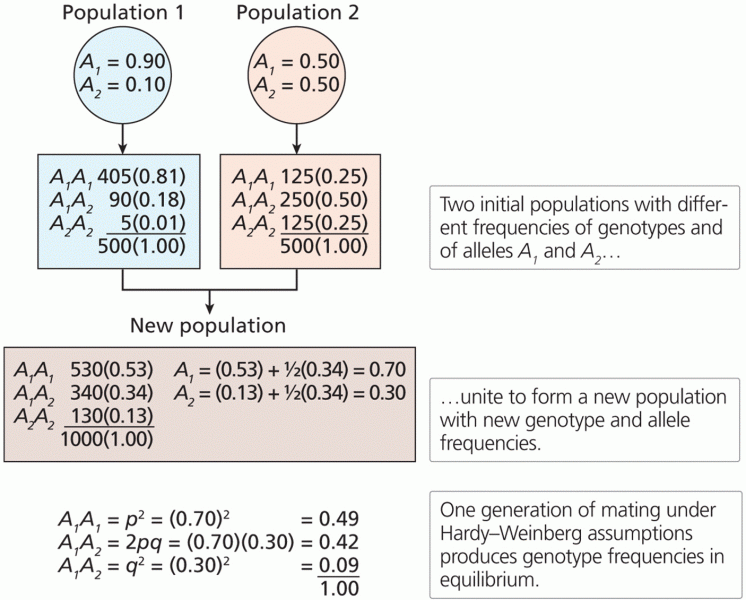
|
|
|
Stroke kills people from all ethnic backgrounds, but the people at highest risk for fatal strokes are: black men, black women, Asian men, white men, and white women.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.