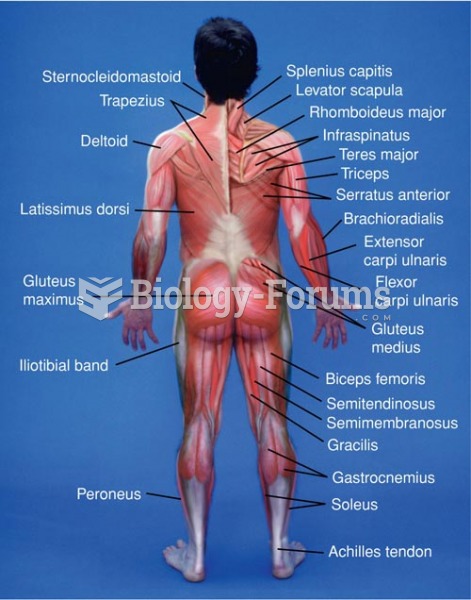
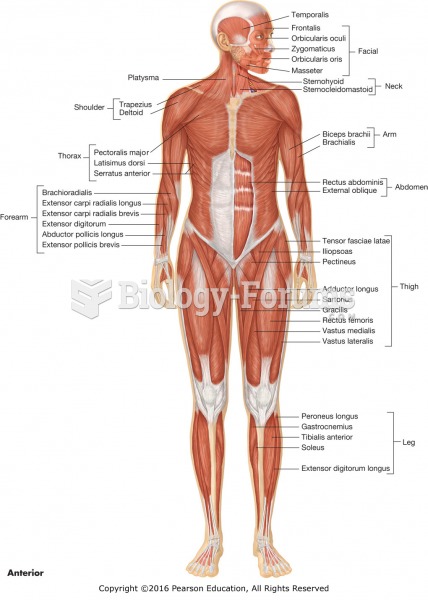
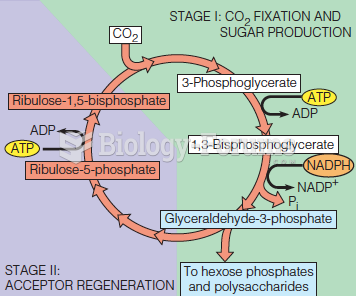
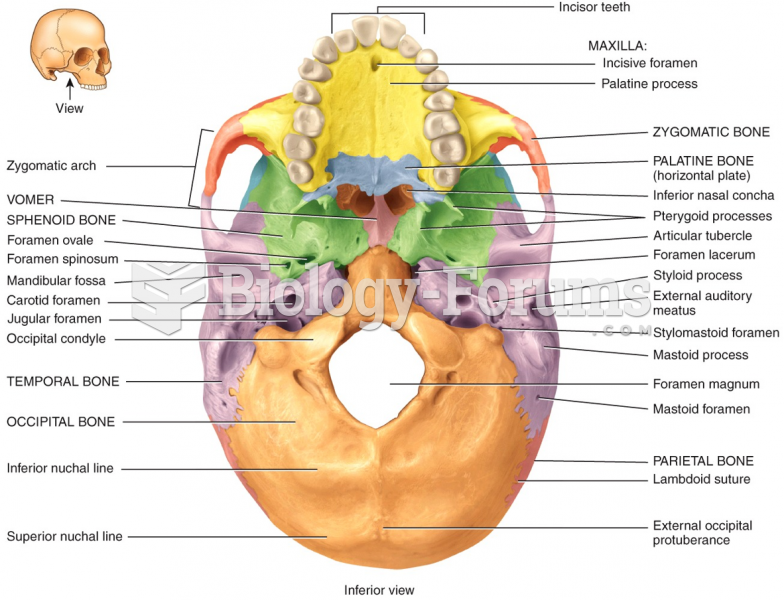
Answer to Question 1
The first three terms come from Kohlberg's theory, within a frame of reference that children actively construct a sense of self and gender and then selectively attend to same-sex models. (a) Basic gender identity is usually present by age three years when the child recognizes that he or she is a boy or girl. (b) Gender stability is characteristic of the next stage, in which children realize that girls will grow up to be women and boys will grow up to be men. (c) Gender consistency, characteristic of the six- to seven-year-old, involves the realization that gender is stable both across time and across situations; in other words, cross-sex play or dressing does not alter one's gender. One outcome of this realization is intensification of the tendency to selectively attend to same-sex models. Martin and Halverson added consideration of (d) in-group/out-group schemas developed by the young child, which allow the child to sort behaviors as gender-appropriate or -inappropriate, and (e) an own-sex schema, which develops as detailed plans of action appropriate to one's sex role. The child is motivated toward behaving consistently with his or her own-sex schema. Consistent with Kohlberg's view is Slaby and Frey's evidence that the gender concept develops sequentially, progressing through Kohlberg's three stages. This sequence has been observed in several cultures. Not consistent with Kohlberg's assertion that a mature understanding of gender is necessary for gender typing and gender-role development is evidence that children show some gender typing even before establishing a basic gender identity. Consistent with the theory of Martin and Halverson is evidence that children are more interested in exploring objects labeled as gender-consistent and recall these items better later. Also consistent with this view is the finding that children tend to forget or distort counter-stereotypical information.
Answer to Question 2
B