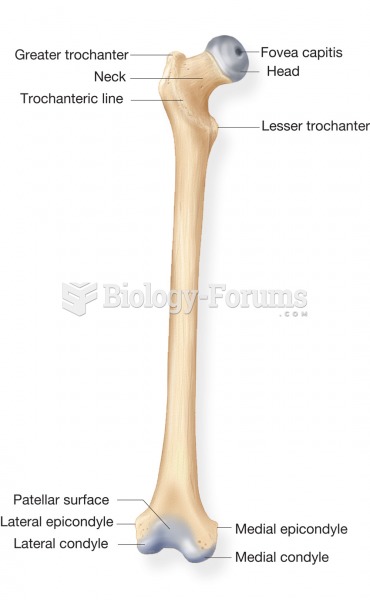
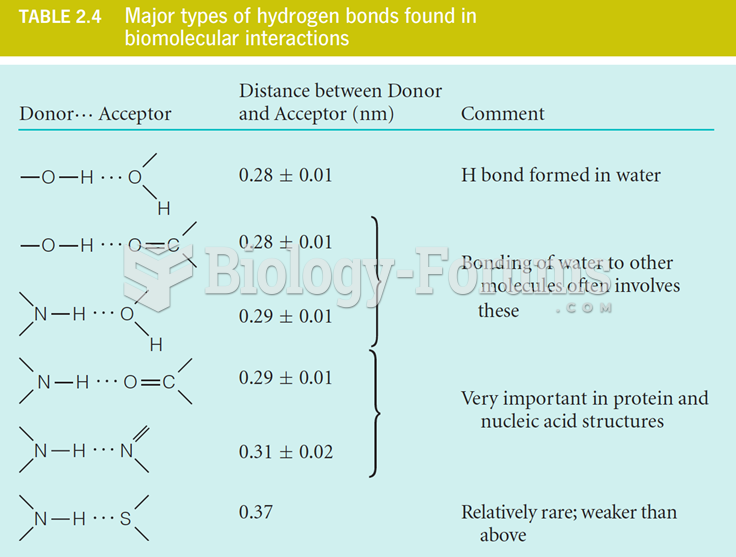
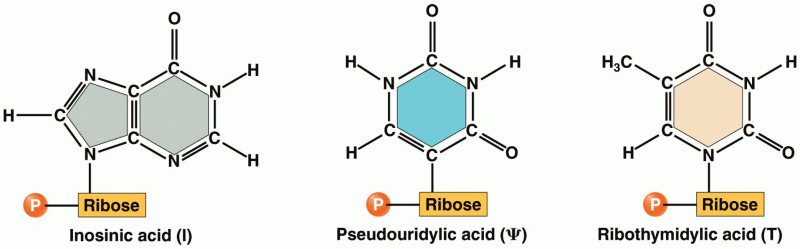
|
|
|
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
Intradermal injections are somewhat difficult to correctly administer because the skin layers are so thin that it is easy to accidentally punch through to the deeper subcutaneous layer.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.