|
|
|
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
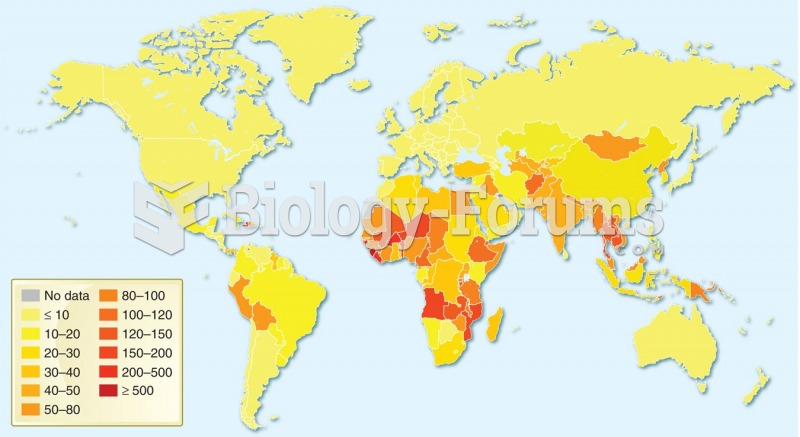
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.