|
|
|
Did you know?
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Did you know?
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
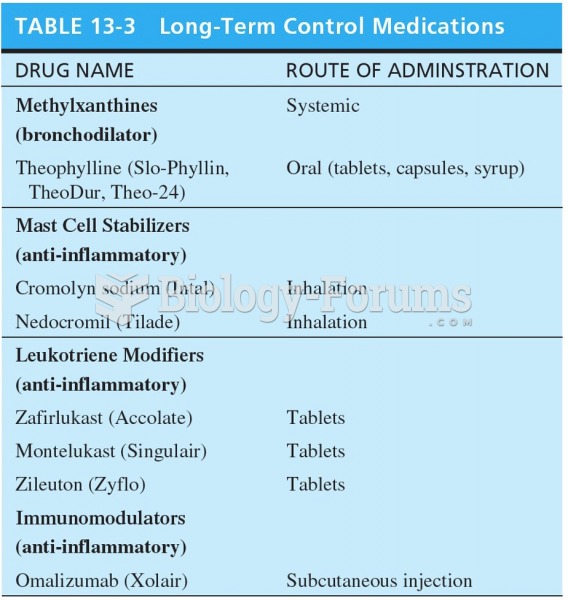
Did you know?
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").