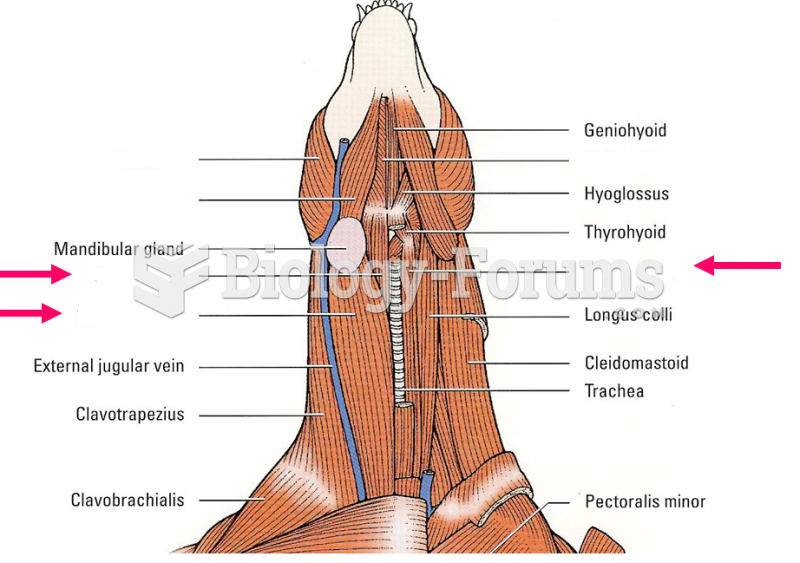
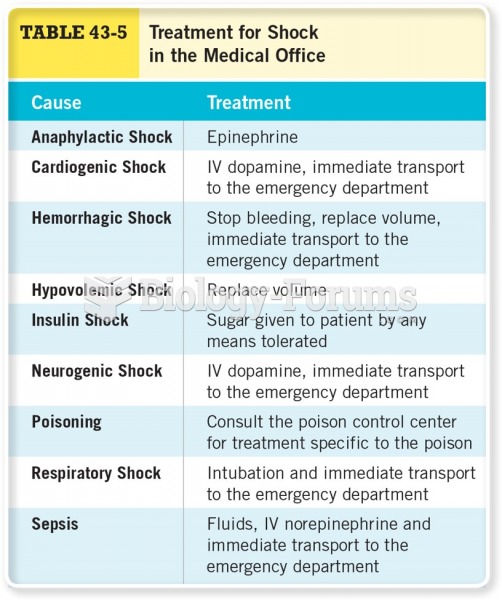
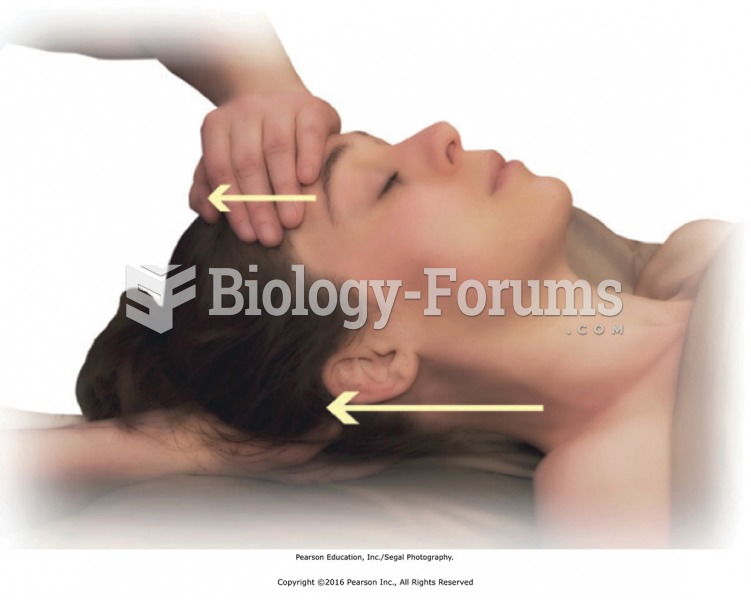
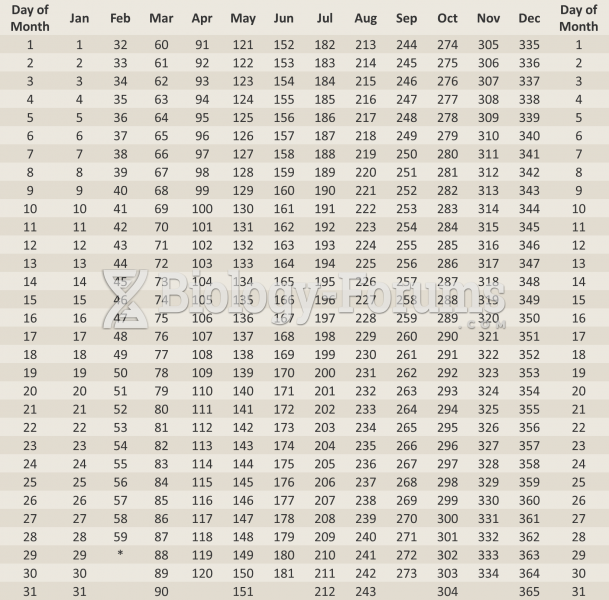
Answer to Question 1
Marcee's diet is high in refined foods. It is likely these food choices are low in the antioxidant vitamins A, C, and E that are necessary for neutralizing free radicals in the body. These foods are typically low in fiber, which acts to bulk up stool volume and assist in removing potential carcinogens from the bowel. A diet high in refined sugar encourages the proliferation of intestinal bacteria that are responsible for converting bile acids to carcinogens. Refined foods that are high in fat stimulate the increased synthesis of bile acids in the liver, providing a greater means for the production of carcinogens by bacteria.
Adenomatous polyps arise when the crypt cells of the intestinal epithelium proliferate in excess of what is needed to replace the cells that normally are shed from the mucosal surface. The cells that produce polyps proliferate in the base of the crypt, continue to replicate at the crypt surfaces (instead of becoming senescent), and express altered apoptosis after arriving at the surface of the epithelium. The changes in cellular differentiation can lead to dysplasia and the development of colorectal cancer.
In ulcerative colitis, inflammatory lesions develop in the crypts of Lieberkhn. Focal hemorrhages emerge that in turn suppurate to form crypt abscesses. The abscesses undergo necrosis and ulcerate. The inflammatory progression eventually produces projections of mucosal tissue that, because they resemble polyps, are termed pseudopolyps.
Because colorectal cancer causes intermittent intestinal bleeding, a fecal occult blood test may be used in conjunction with other screening tests to determine the presence of cancer. The patient is instructed to avoid vitamin C supplements, citrus fruits, and red meat for 3 days before the test to reduce the risk of false-positive results. NSAID use is halted 7 days before administering the test. The process using the guaiac-based test involves the preparation of two fecal slides from three consecutive bowel movements. The results are easy to obtain and can be assessed at the site of the health care provider.
Answer to Question 2
Liver disease contributes to anemia and clotting disorders in a number of ways. Fibrinogen and clotting factor production is decreased with impaired liver function. Malabsorption of vitamin K contributes to clotting insufficiency. Alterations in fat metabolism affect the phospholipid cell membrane of red blood cells and cause hemolysis. The development of splenomegaly and hypersplenism results in the decrease of all formed elements of the blood; anemia, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia are all manifestations of hypersplenism. Finally, folic acid deficiency produces megaloblastic anemia.
Esophageal varices occur in those with liver disease and are associated with a high mortality rate due to hemorrhage. Varices develop as a result of portal hypertension. The increased portal vein pressure encourages the development of portosystemic shunts. A collateral circulation between the portal vein and coronary vein produces dilation of the esophageal veins.
Acute pancreatitis is sometimes seen in the alcoholics, particularly after binge drinking. Why are tachycardia and hypotension indications of this condition?
Acute pancreatitis causes a fluid shift into the retroperitoneal and abdominal cavity, including the peripancreatic spaces. The lowered blood volume results in hypotension and compensatory tachycardia.
Three pathways exist in the liver for the metabolism of alcohol, and all mechanisms produce the toxic metabolite acetaldehyde. One such mechanism is the alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) system. In males, the ADH system is depressed by testosterone. Women therefore produce more acetaldehyde and are more likely to receive alcohol-induced liver damage than men.