|
|
|
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
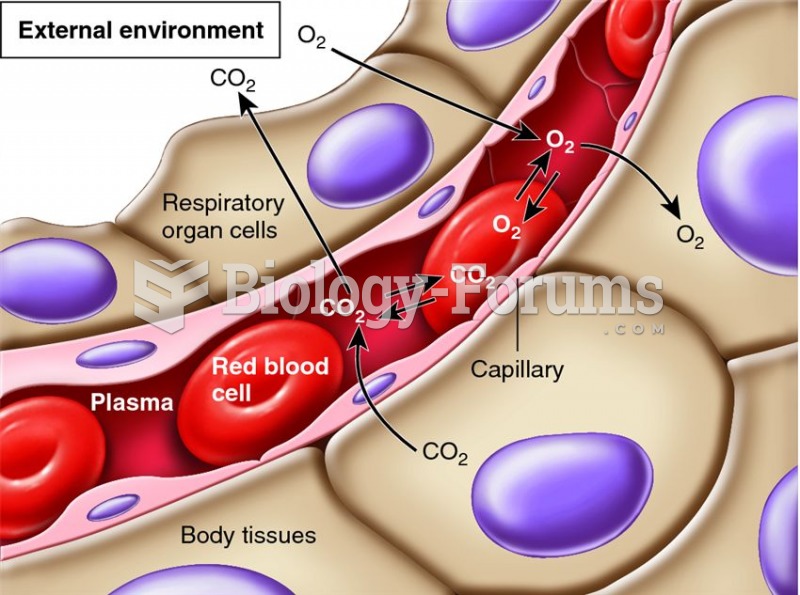
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.