|
|
|
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
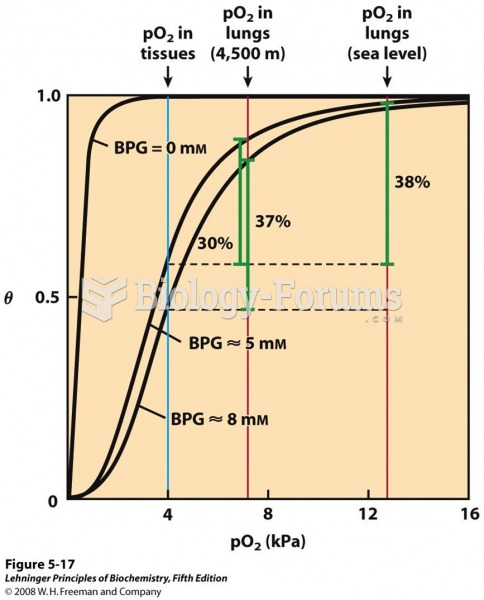
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.