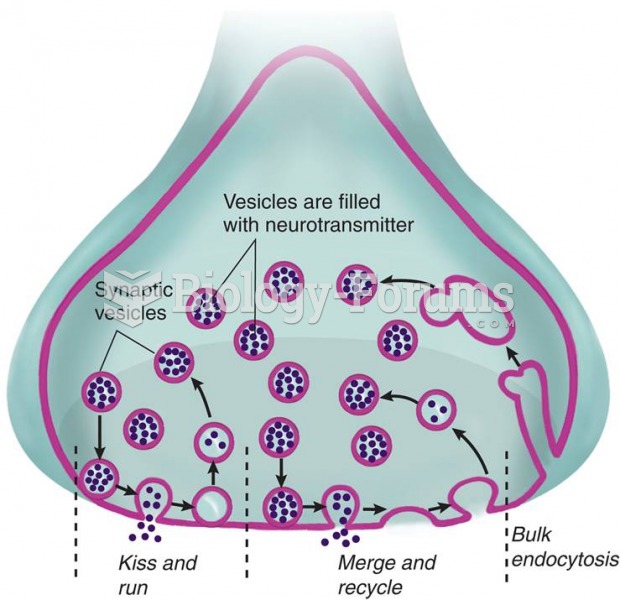
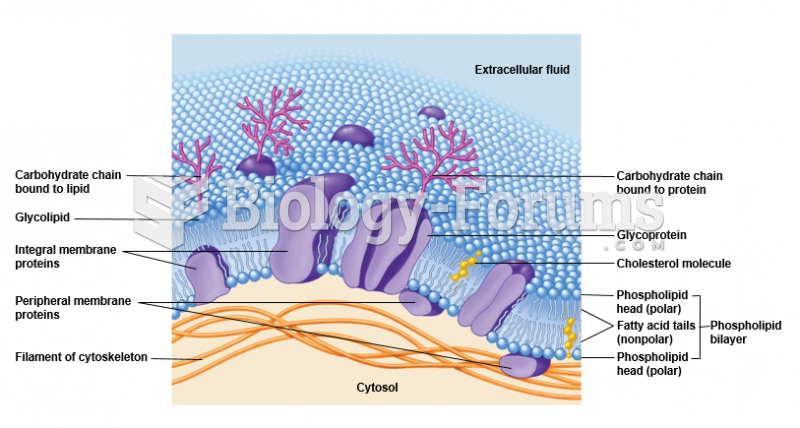
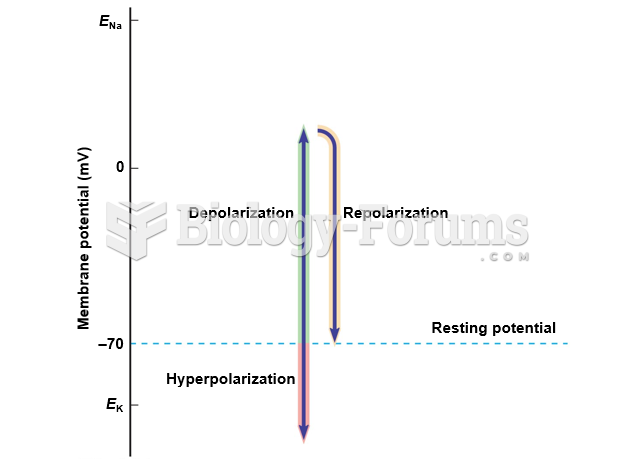
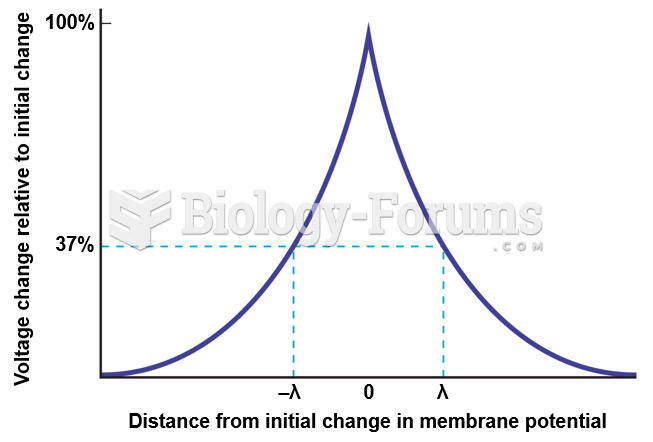
|
|
|
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
Did you know?
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
Did you know?
More than one-third of adult Americans are obese. Diseases that kill the largest number of people annually, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and hypertension, can be attributed to diet.