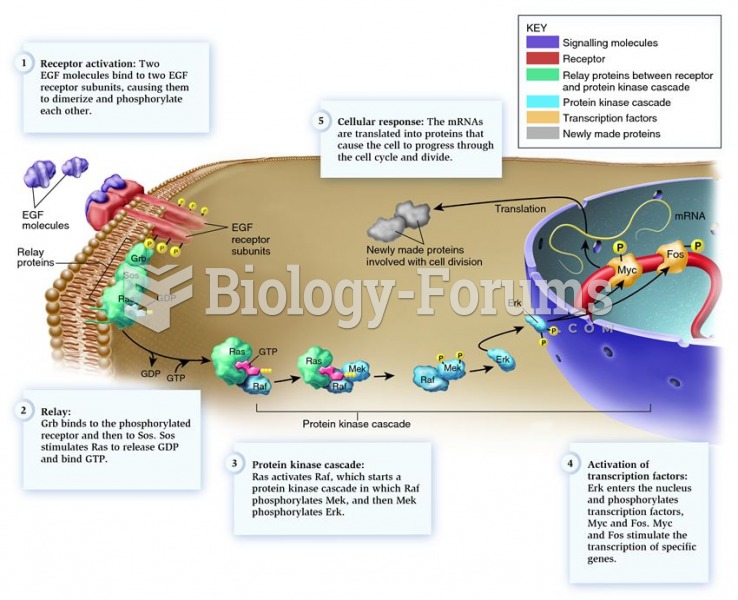
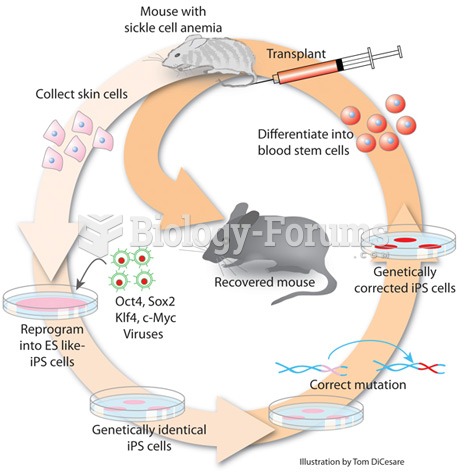
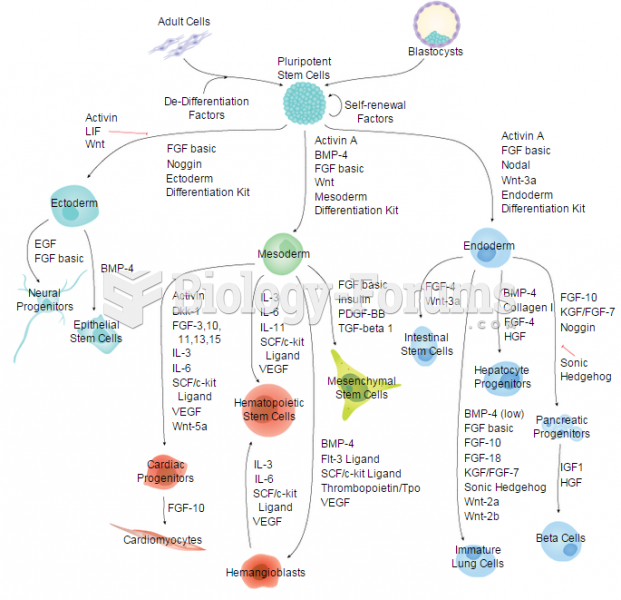
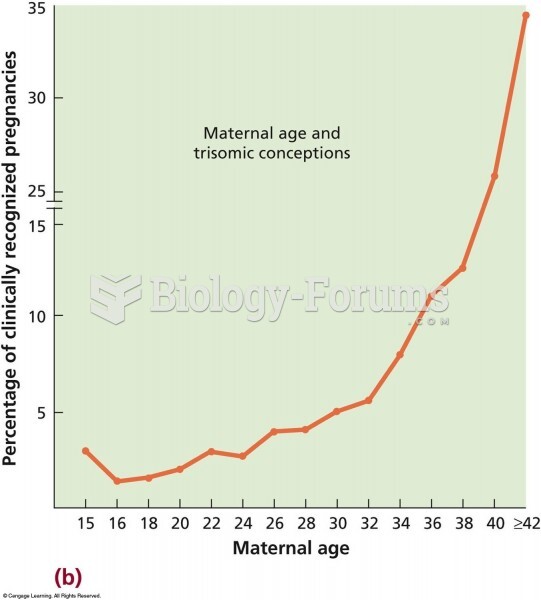
|
|
|
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.