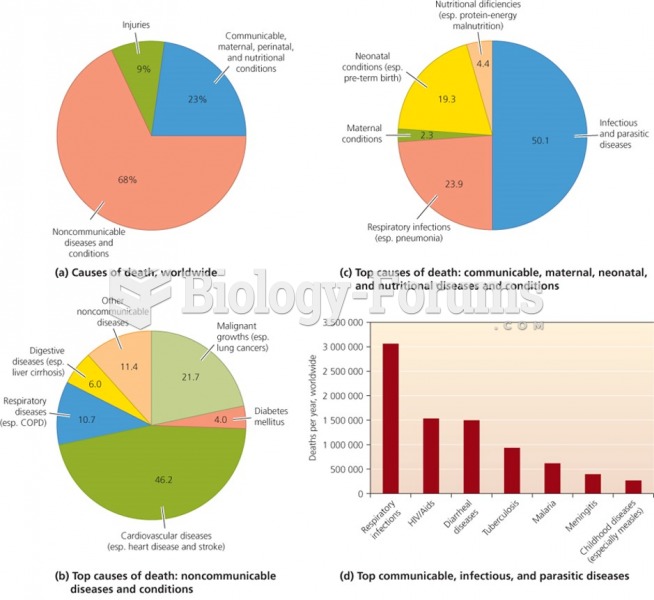
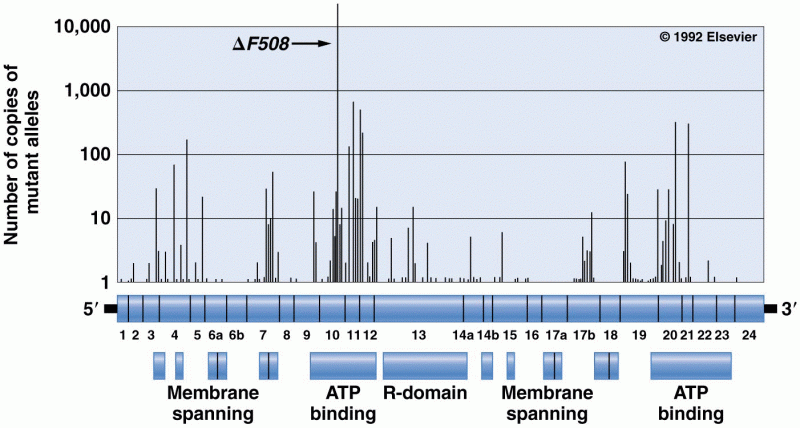
Answer to Question 1
Answer: Disseminated intravascular coagulation is a systemic condition but is not a disease itself. Patients with pre-existing conditions who often have no significant correlation to coagulation have increased risk for developing DIC through specific trigger mechanisms. The mechanisms include endothelial cell damage, tissue injury, hypoxia, exposure of tissue factor, platelet activation, endotoxin release, thrombotic disease, immune complexes, and secretion of proteolytic enzymes. Any of these triggers can stimulate the formation of multiple microthrombi in intravascular circulation because of the formation of thrombin, which ultimately leads to the pathophysiology of DIC. Thrombin causes platelet activation; excessive fibrinolysis; consumption of coagulation procoagulants, including fibrin formation; and consumption of regulatory coagulation control proteins.
Because of this consumptive coagulopathy, laboratory analysis will detect several aberrant results. At the screening level, these include:
A decreased platelet count as the result of platelet consumption by formation of microthrombi
A prolonged PT/APTT because of the lack of available factors in vitro.
Other test results that can be used to confirm DIC include:
Decreased Fibrinogen because of increased fibrinolysis and increased fibrin monomer formation.
Decreased Protein C and S because they will also be consumed with the formation of excess thrombin.
Increased D-dimer as a result of excessive fibrinolysis
Fibrin can deposit in the lumen of the blood vessels of patients with DIC. As cellular components travel through circulation, they will come into contact with fibrin and therefore show evidence of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ( with schistocytes and spherocytes).
Answer to Question 2
Answer: von Willebrand's disease results from a deficiency in VWF, which has several essential functions in coagulation as (a) carrier protein for factor VIII: C and (b) interaction of platelet glycoprotein Ib/IX to subendothelial collagen that results in platelet adhesion. As a result of this, VWD patients exhibit signs of primary hemostatic pathway anomalies, which include mucocutaneous systemic bleeding and petechiae.
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is an inherited qualitative disorder that results in a defective glycoprotein Ib/IX receptor. As a result, the BSS patient exhibits signs of primary hemostatic pathway anomalies, much like with VWD. From a clinical standpoint, VWD and BSS appear very similar.
In regard to the screening tests, both disorders yield similar results. Standard screen for primary hemostatic anomalies is abnormal in both cases.
The main difference between the two is in multimer analysis and factor VIII: C levels. Because VWF is needed as a carrier protein for factor VIII: C, a patient with VWD will show decreased activity with factor VIII: C. Conversely, BSS will show normal levels. In addition, multimer analysis will be abnormal (because it assesses VWF multimers) in most cases of VWD, whereas in BSS, it will be normal.