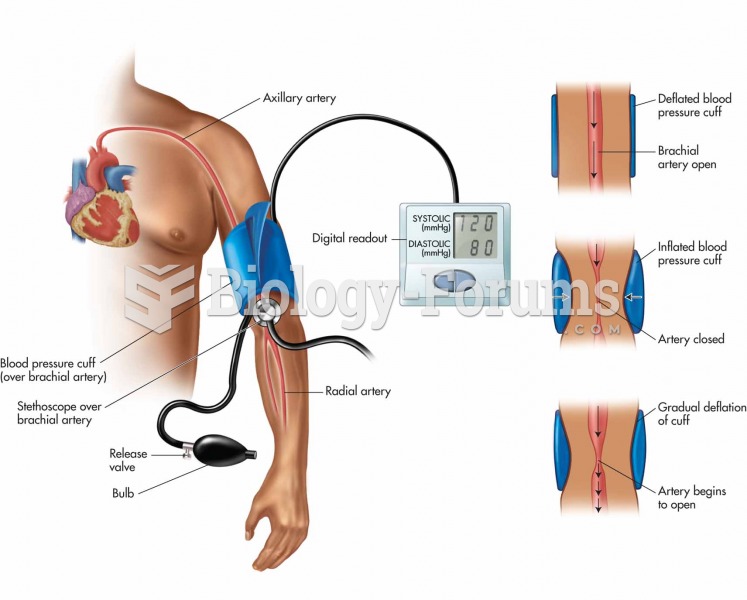
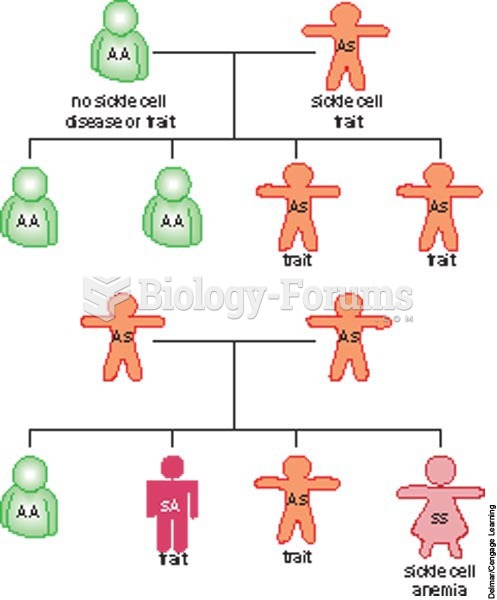
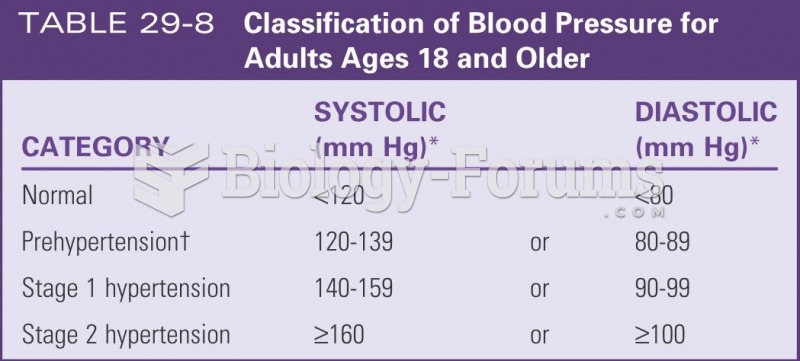
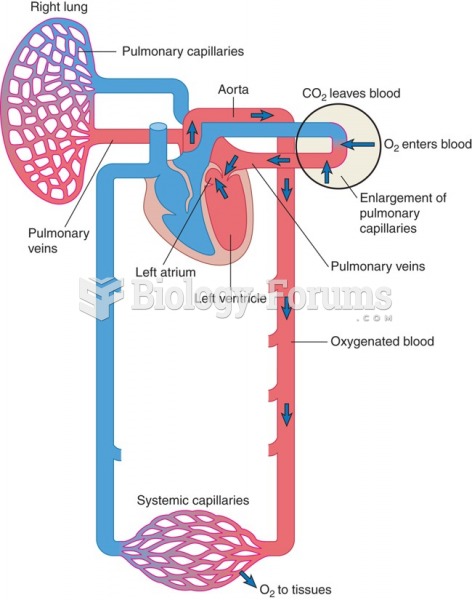
|
|
|
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.