|
|
|
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
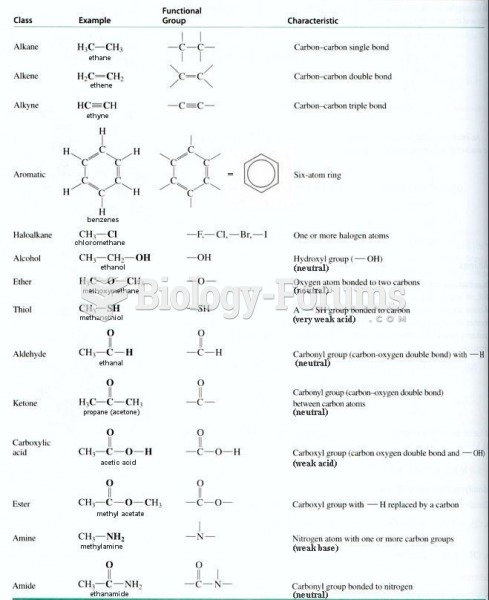
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.