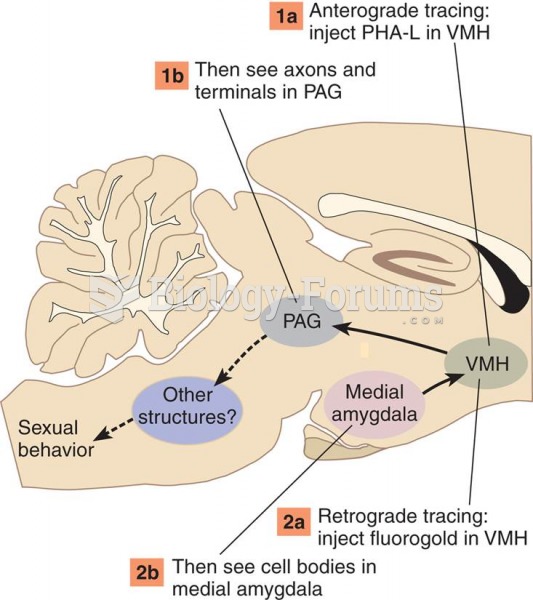
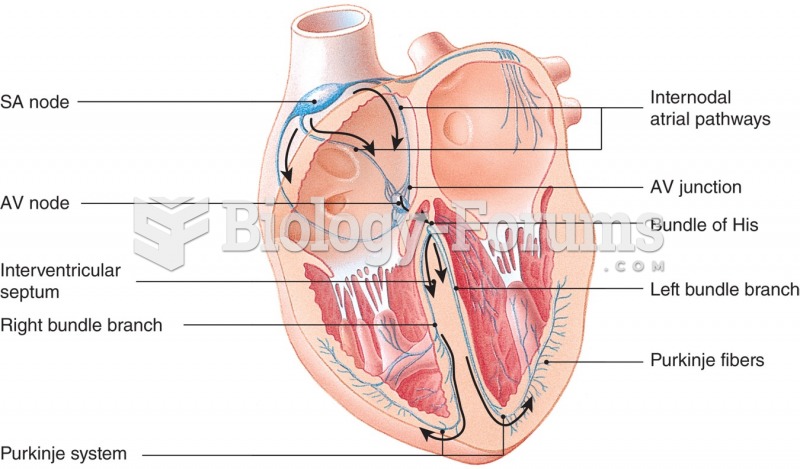
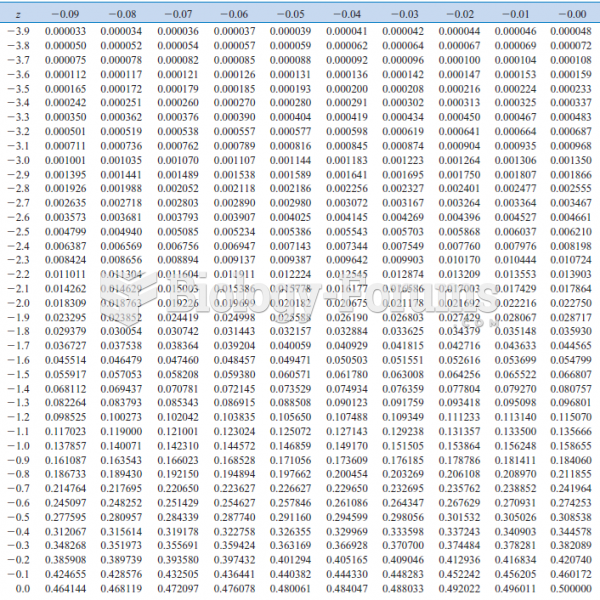
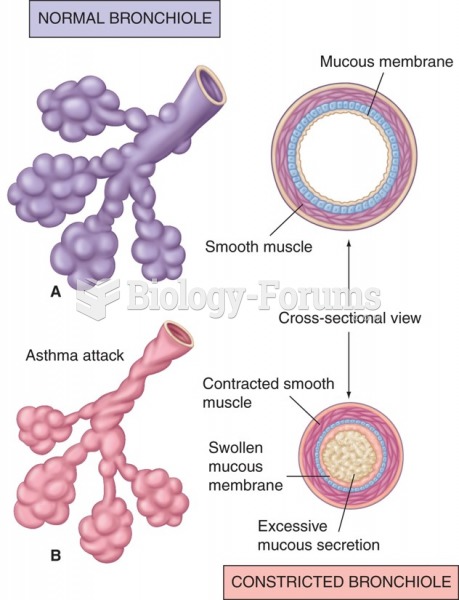
|
|
|
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.