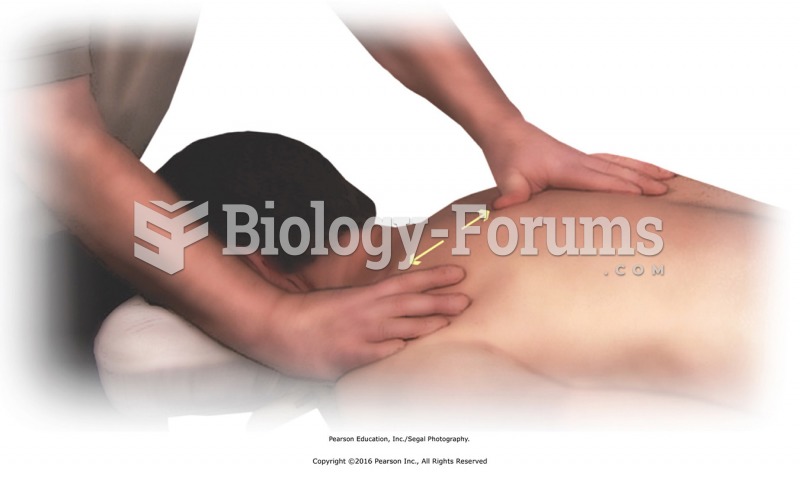
|
|
|
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
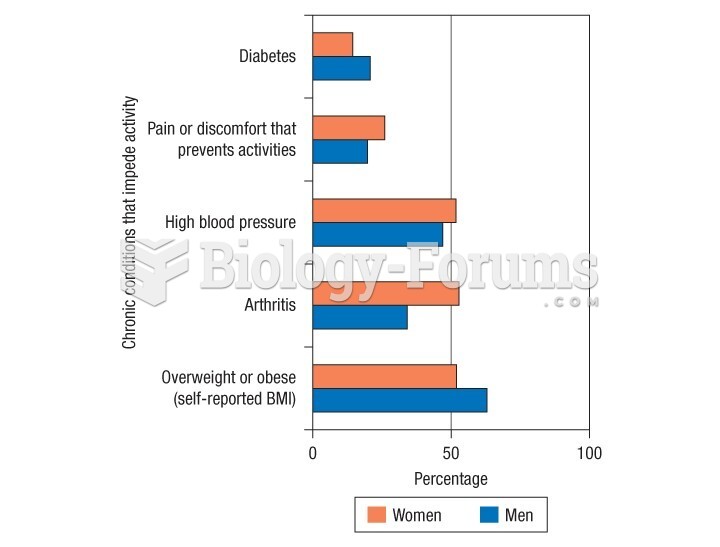
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
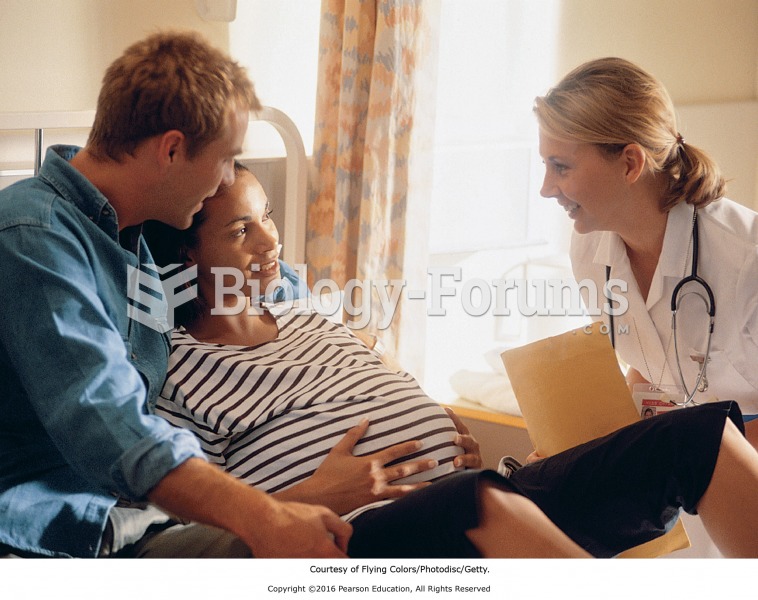 Teaching women about the safety of drug use during pregnancy is an essential component of nursing ...
Teaching women about the safety of drug use during pregnancy is an essential component of nursing ...
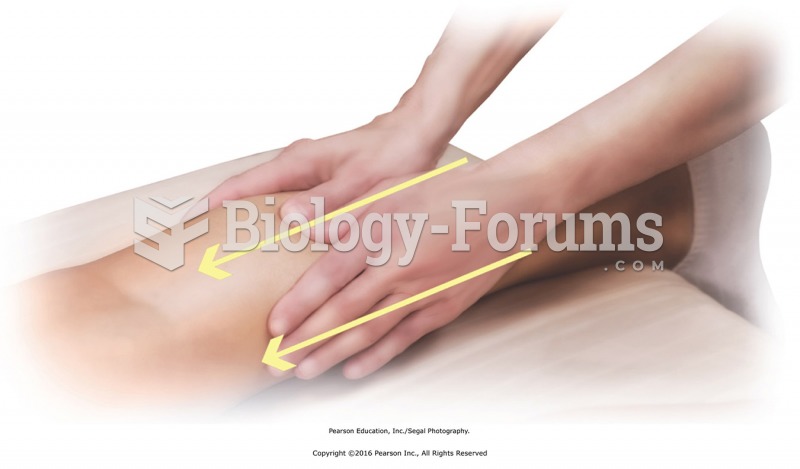 Apply stroking from ankle to knee, using both palms to slide along the calf muscles. If hands will ...
Apply stroking from ankle to knee, using both palms to slide along the calf muscles. If hands will ...
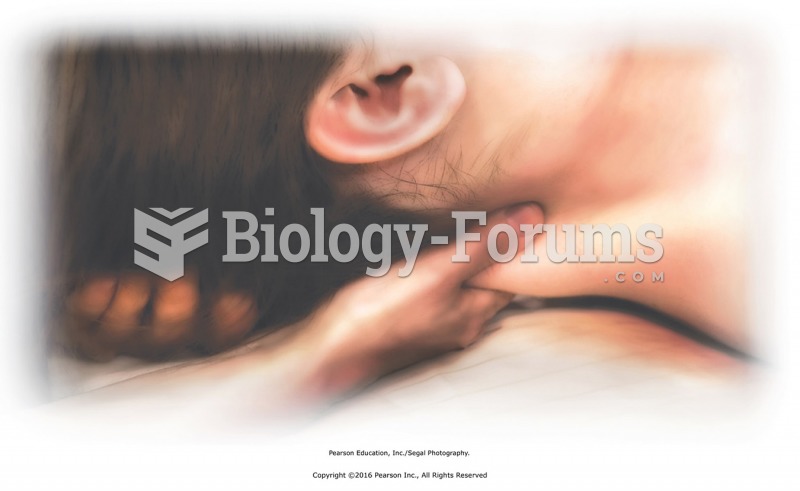 Apply warming petrissage to cervical muscles with neck in slight traction. Traction neck with one ...
Apply warming petrissage to cervical muscles with neck in slight traction. Traction neck with one ...