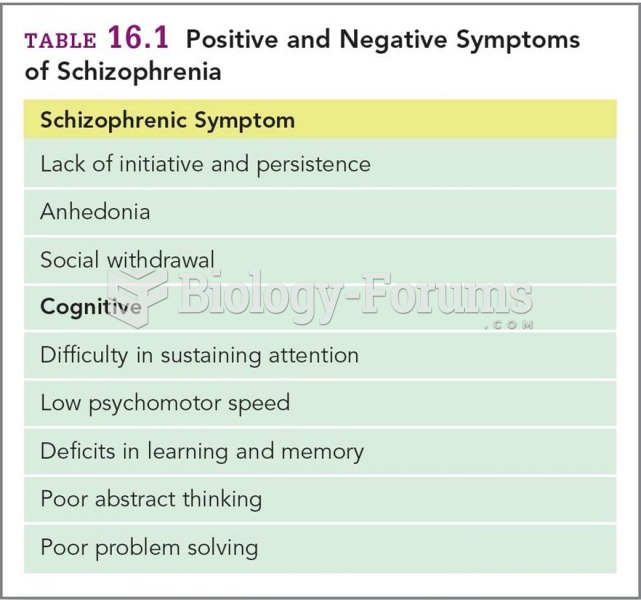
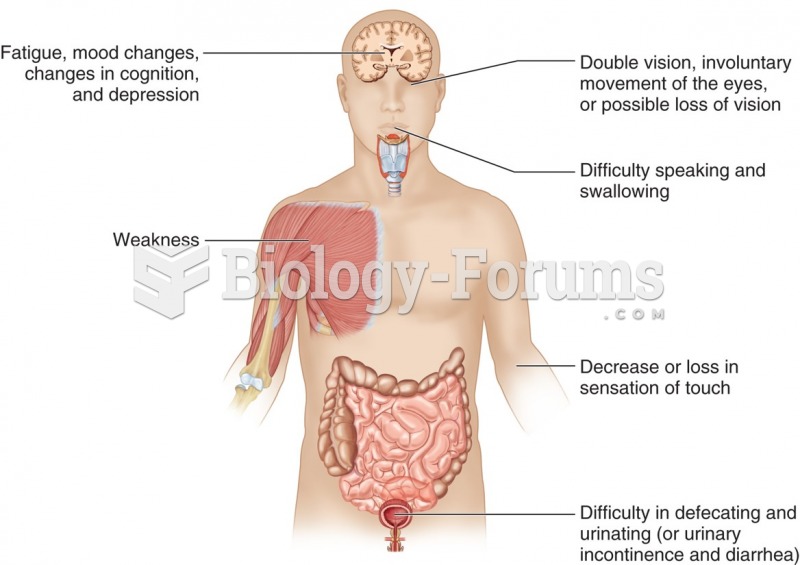
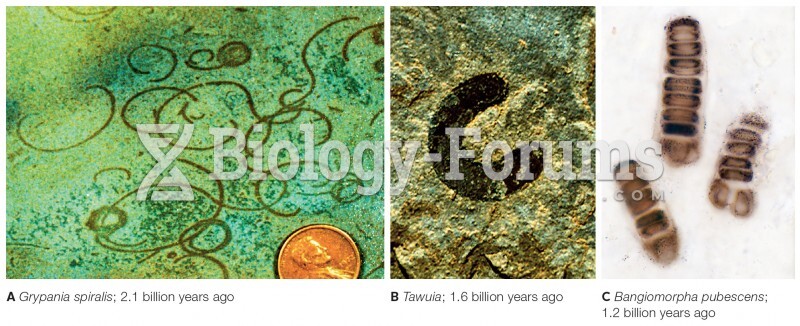
|
|
|
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
Did you know?
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
Did you know?
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.