Answer to Question 1
ANS: D
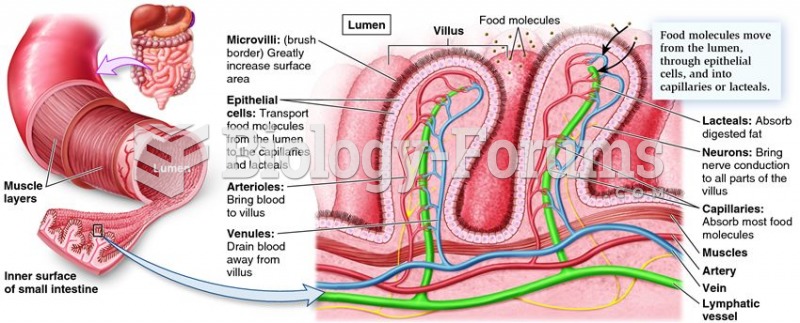
A fetus may be found to be of a size that is not commensurate with normal growth rates (size not equal to dates) when the uterine size is measured and evaluated during routine prenatal visits. First-trimester uterine sizes are usually determined with bimanual examination, and size-date discrepancies are often not clinically relevant. After 20 weeks of gestation, fundal height measurements begin to correlate (within 2 cm) with gestational age. The fundus should be at the level of the umbilicus at 20 weeks of gestation, and it rises 1 cm per week until 32 weeks of gestation. False small-for-dates presentations may result from inaccurate LMP dates, varying menstrual cycle lengths, improper fundal height measurement, or a fetus in a transverse lie. Differential diagnoses include intrauterine growth restriction (either asymmetric or symmetric), which affects about 5 of the general population and as much as 10 of high-risk populations (Table 19.9); constitutionally small fetus; inaccurate pregnancy dating; improper fundal height measurement; transverse lie of the fetus; and oligohydramnios.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: B
Preterm labor is the onset of labor before 37 completed weeks of gestation. The accurate diagnosis of preterm labor is critical but often difficult. Fewer than half of the women who have four or more contractions per hour will deliver in 7 to 14 days of the preterm labor assessment. The diagnosis may be confirmed when there is a cervical dilatation of 3 cm or more in a woman without persistent contractions. Women who are having persistent contractions need a cervical change of at least 1 cm, a dilatation of 2 cm or more, or a positive fetal fibronectin assay for diagnosis (Bernhardt & Dorman, 2004). If the diagnosis is not confirmed, but the index of suspicion remains high, it is entirely reasonable to repeat the cervical examination at a later time. Transabdominal ultrasounds and home uterine activity monitoring have also been used in an effort to identify preterm labor but with mixed results.