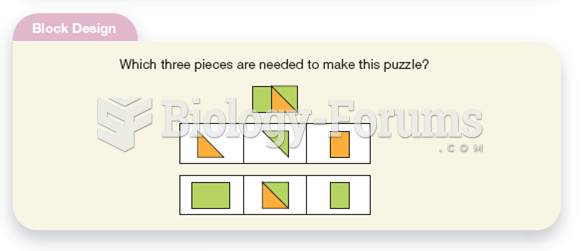
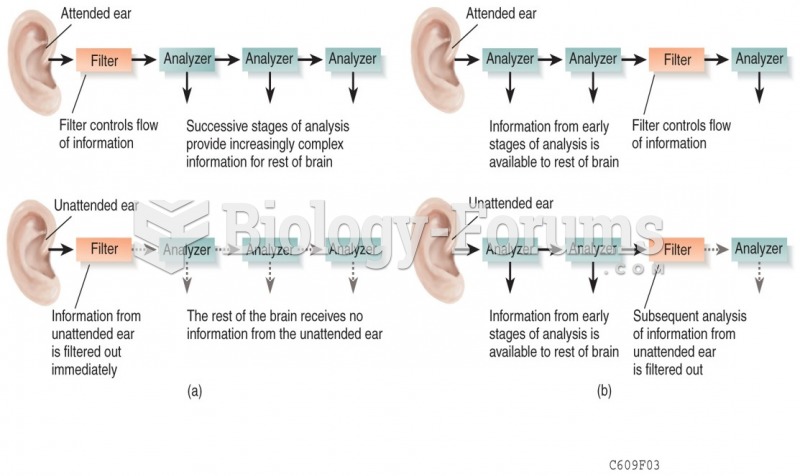
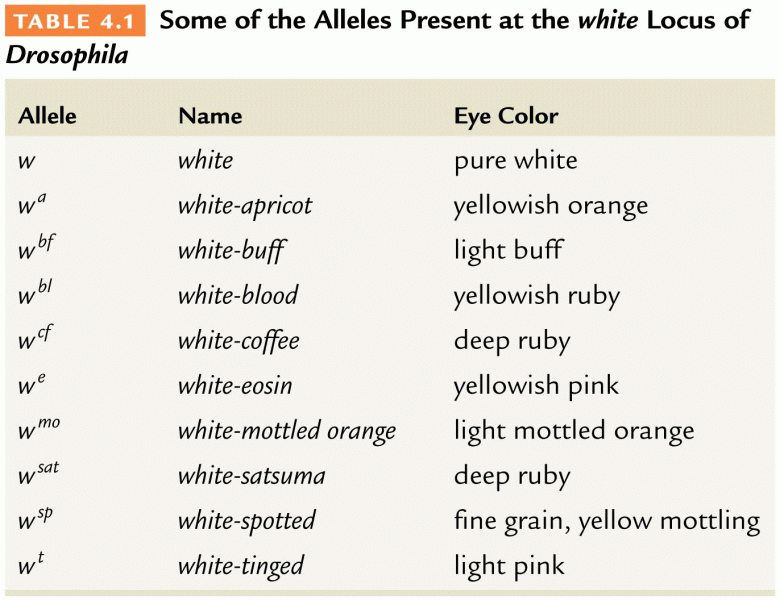
|
|
|
Everyone has one nostril that is larger than the other.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.