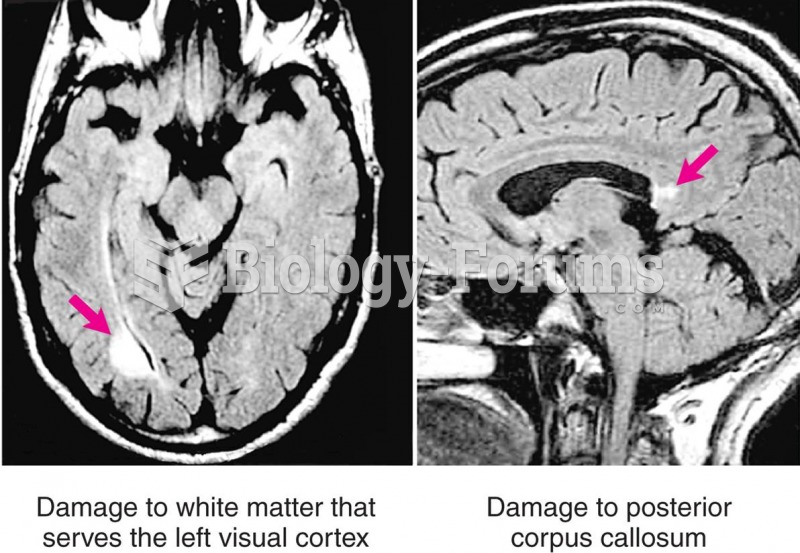
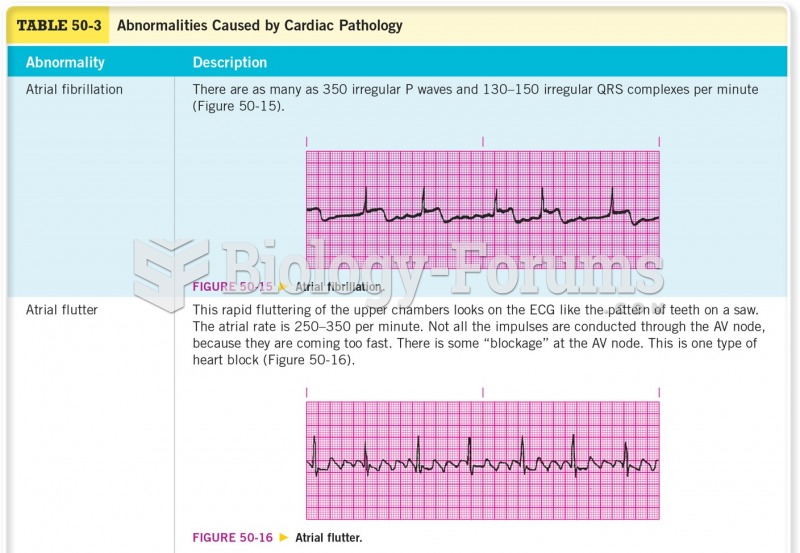
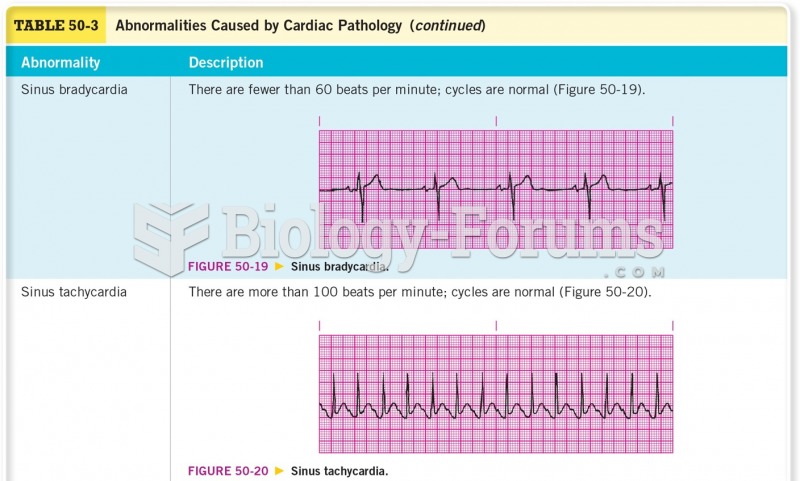
|
|
|
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Did you know?
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
Did you know?
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
Did you know?
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Did you know?
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.