|
|
|
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
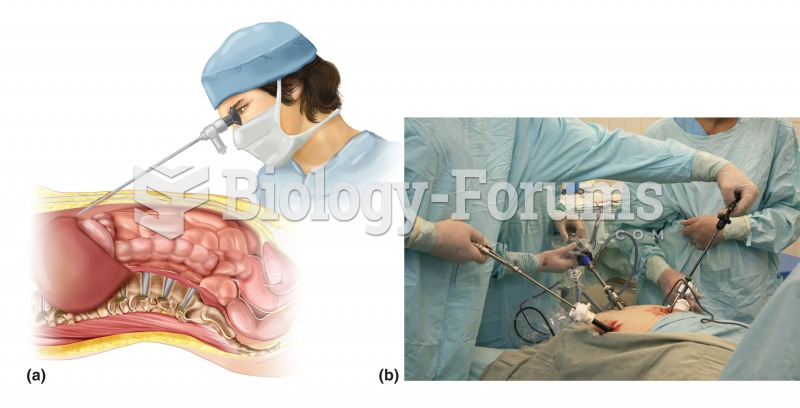
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
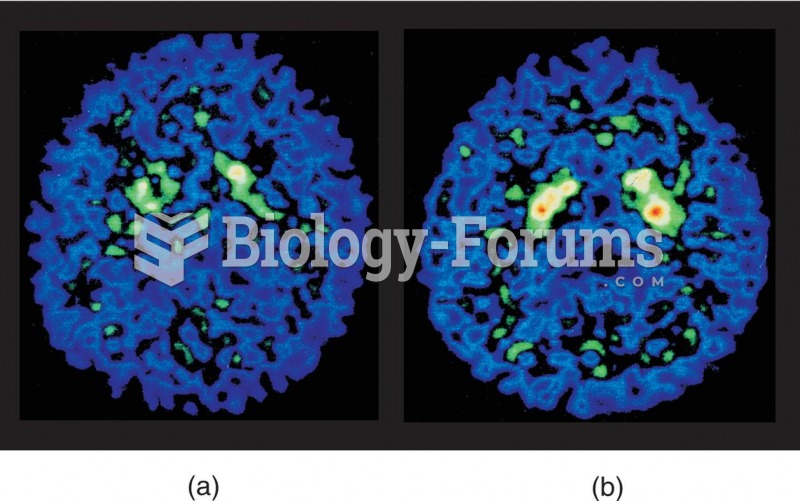
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.