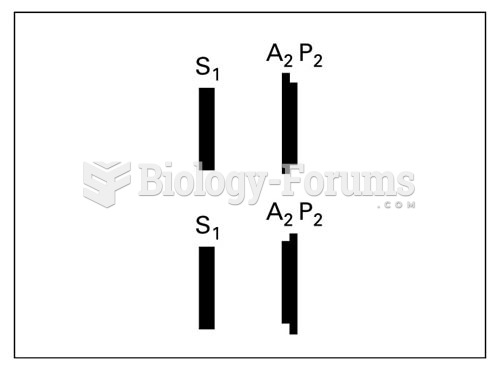
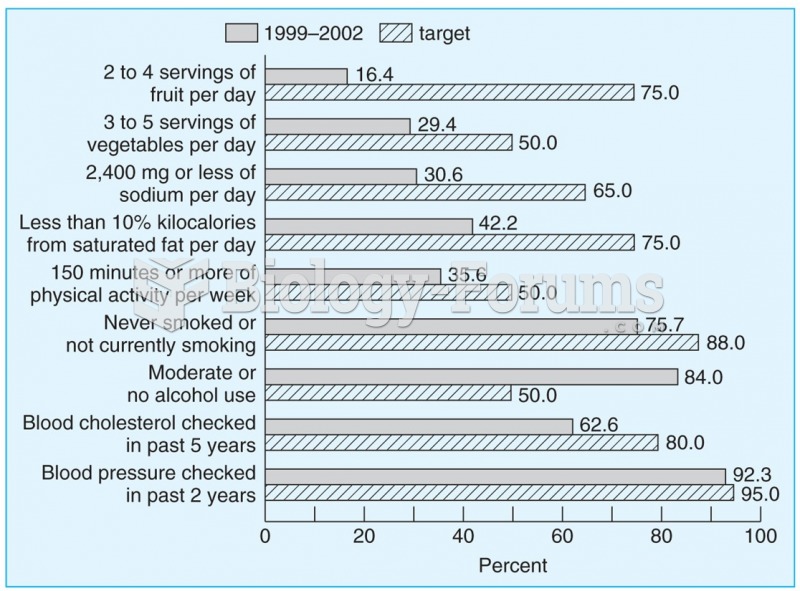
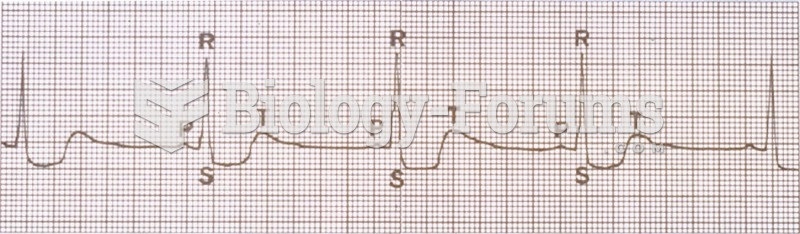
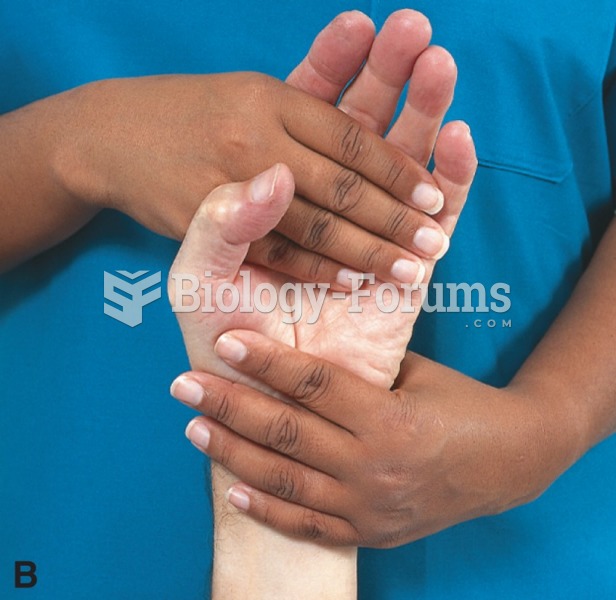
|
|
|
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.