|
|
|
Did you know?
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
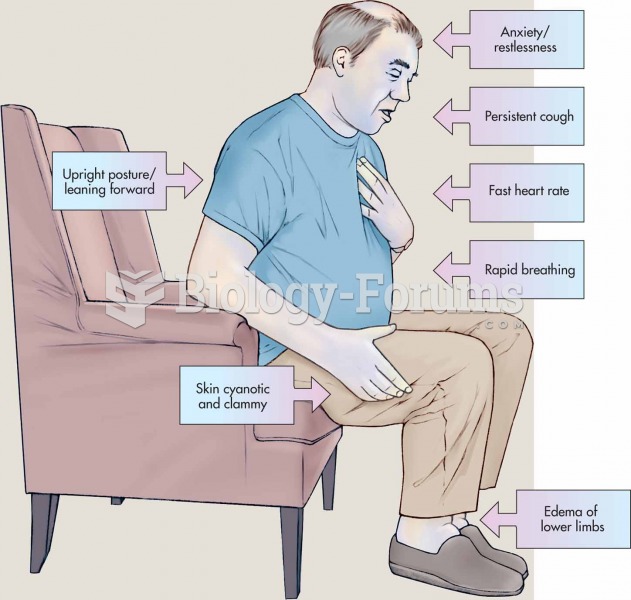
Did you know?
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
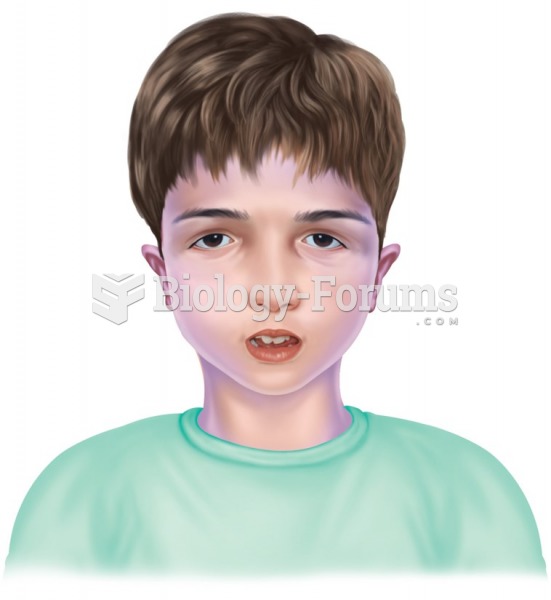
Did you know?
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Did you know?
Human stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve small pieces of metal such as razor blades or staples.