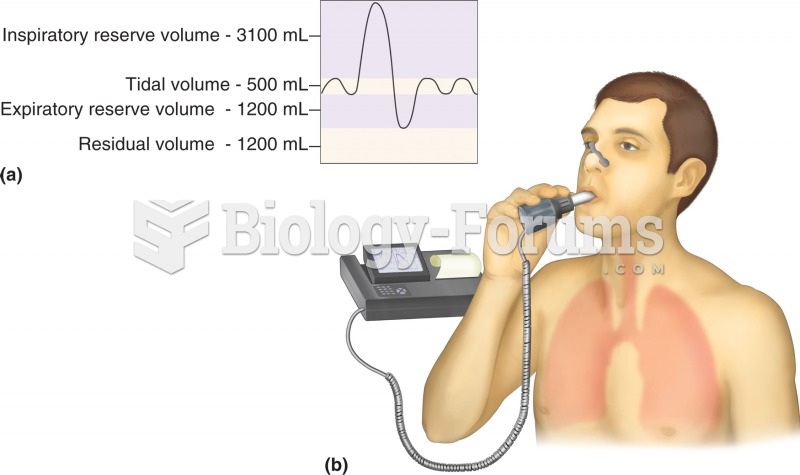
|
|
|
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
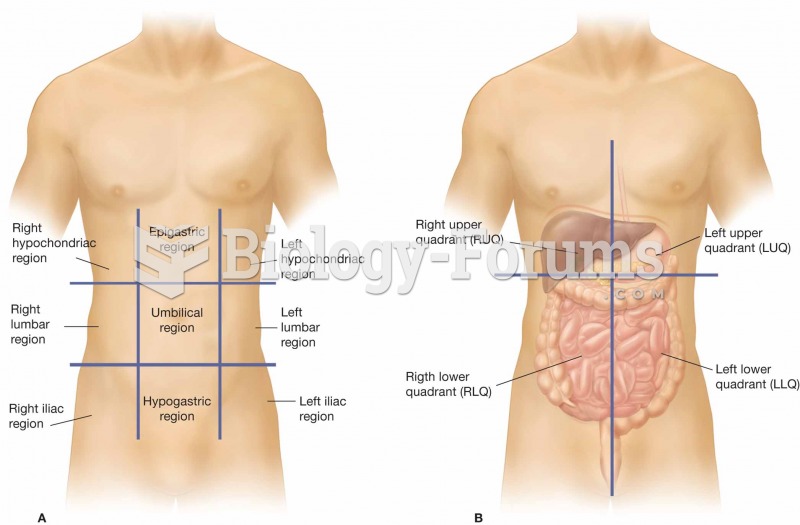 (A) The nine regions of the abdominopelvic cavity. (B) The four regions of the abdomen, which are re
(A) The nine regions of the abdominopelvic cavity. (B) The four regions of the abdomen, which are re
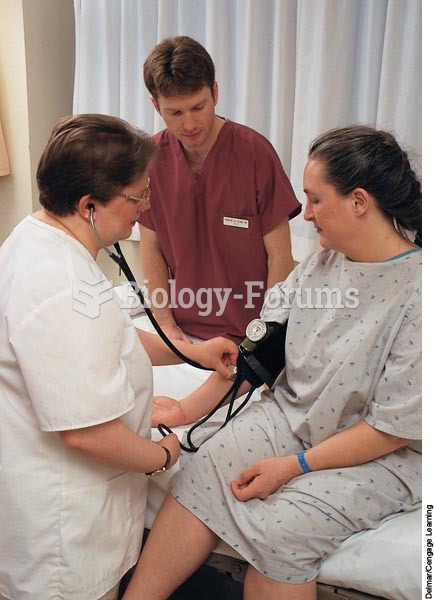 Vital signs for clients in metabolic alkalosis may reveal hypotension, bradycardia, and an irregular
Vital signs for clients in metabolic alkalosis may reveal hypotension, bradycardia, and an irregular