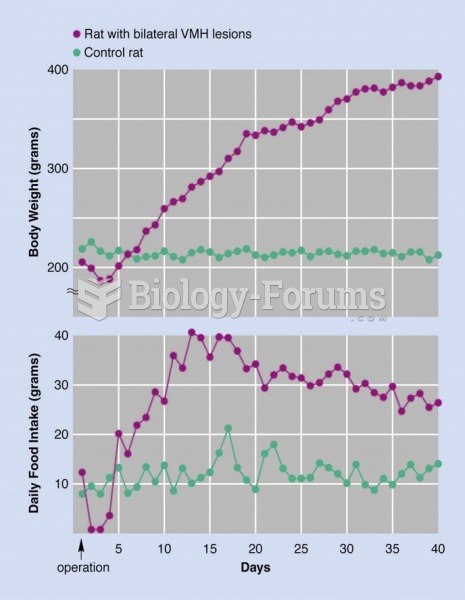
|
|
|
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
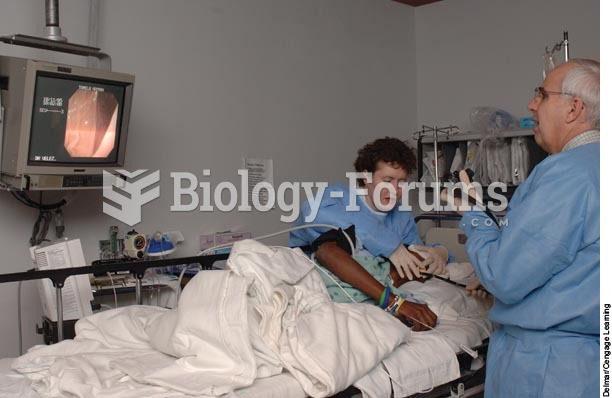 A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
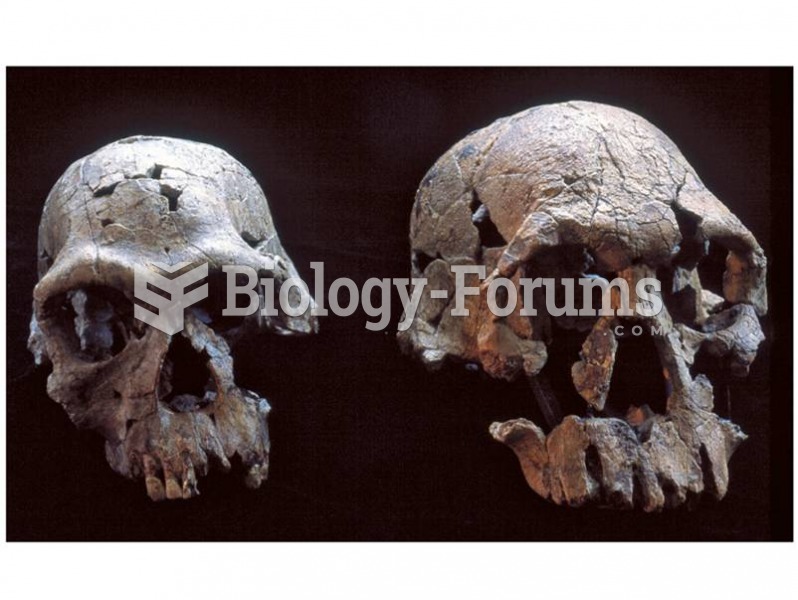 The crania, and especially the faces of KNM-ER 1813 and 1470, differ enough that some scientists inc
The crania, and especially the faces of KNM-ER 1813 and 1470, differ enough that some scientists inc