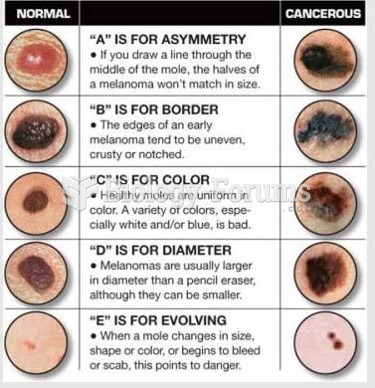
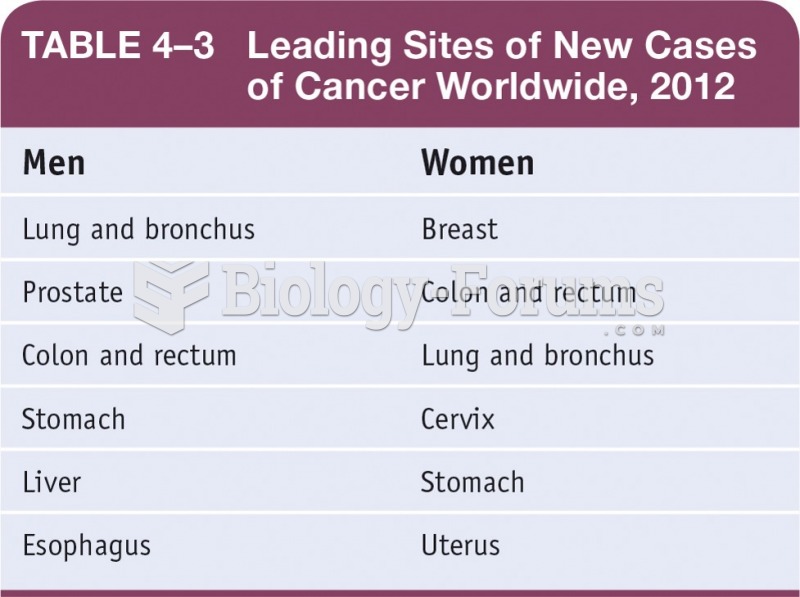
|
|
|
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.