|
|
|
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
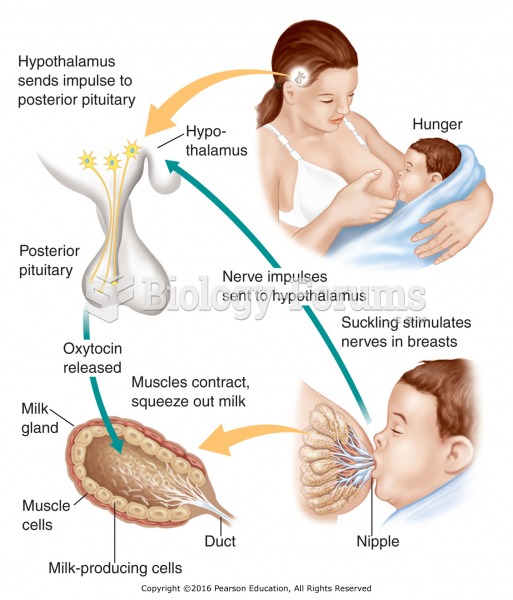
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.