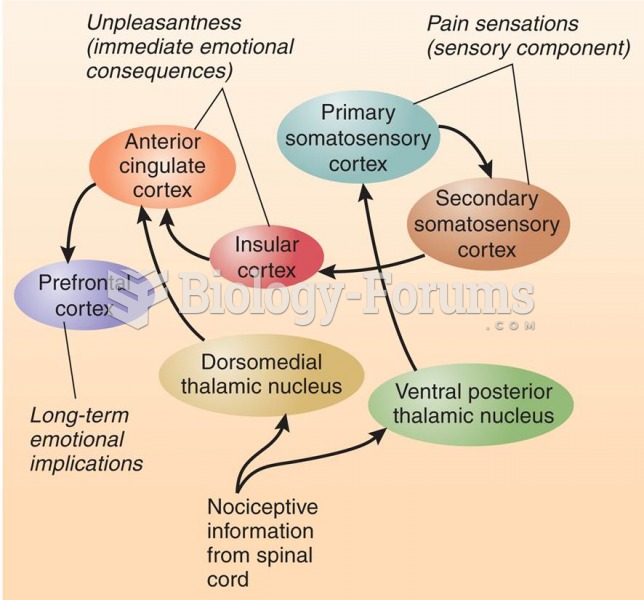
SUBJECTIVE: The patient is here complaining of a (1)________ of her arthritic pain. She gets arthritic pain in her knees, ankle, back, and spine. She has a problem taking (2)________ secondary to GI upset. The patient has a history of rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, (3)________, and osteoarthritis. She is currently on Plaquenil. She had to self-discontinue her (4)________ secondary to GI upset. She also takes a Bayer aspirin each day. This is a longstanding problem, and the patient has no new acute changes.
OBJECTIVE: HEENT unremarkable. (5)________ Regular rate and rhythm without murmur. Lungs CTA. Extremities: No (6)________ edema. Musculoskeletal: No joint (7)________ or edema. There are no rheumatoid (8)________ noted.
ASSESSMENT/PLAN:
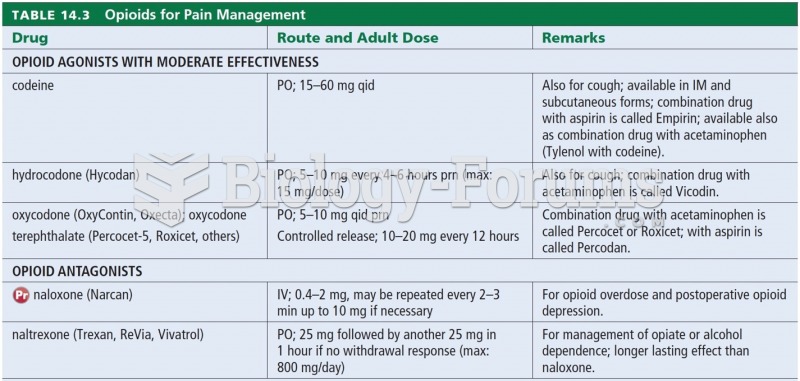
1. Rheumatoid arthritis, with (9)_______ pain. Patient is to continue with her Plaquenil. Will give trial of Arthrotec 50 mg daily to t.i.d. as her GI tract tolerates, 100, refill 1 prescription given.
2. Plaquenil use. Will check CBC and CMP today. Will also check (10)________, TSH, and lipid panel, as these are required at this time.
Question 2
CLINIC NOTE
SUBJECTIVE: Patient is a 72-year-old female with known osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis. She says she fell October 29 and landed on her right buttock and hip while missing a step. She stated that she was looked at the time by a nurse who happened to be in the area. She felt okay and got up and moved about without any problems. Last week she had the onset of aching intermittently in the right anterior thigh up to the lateral aspect of the hip with activity. When she rests, it goes away. She has no coldness of the extremity, restriction of movement from her usual baseline, or (1)________. Patient is otherwise at her baseline state of health.
OBJECTIVE: Musculoskeletal: Back has full range of motion, with forward and backward bending, as well as sideward bending. Lower extremities have 5/5 muscle strength with 2/4 (2)________ reflex. Neurovascular is intact. There is no muscular tenderness at this time. Negative pelvic (3)________. Negative (4)________. No skin changes.
ASSESSMENT/PLAN: Musculoskeletal pain. Rule out fracture in patient with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthrotec 50 mg b.i.d. to t.i.d. to current (5)________. Rest and warm heat. Will follow up as dictated by x-ray and otherwise on a p.r.n. basis.