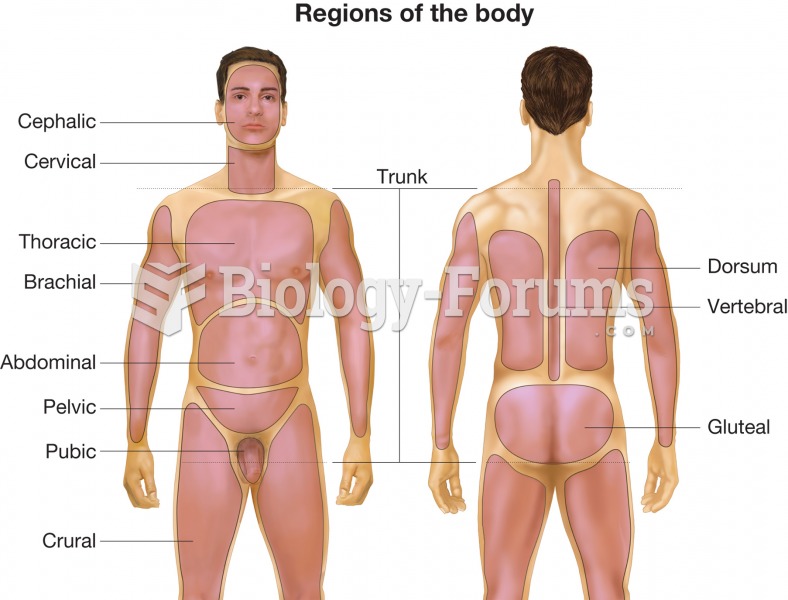
Using the 1995 body area/organ system physical examination, the documentation supports a comprehensive physical examination.
Cassidy presents to the Collegetown Clinic today for evaluation of throat pain and productive cough.
29-year-old woman is a new patient presenting with worsening daytime cough. Over the past three weeks, cough has become more persistent and hoarse, but cough does not interrupt sleep. Throat burns constantly during day. No identified postnasal drip, although patient rates throat pain at 8/10 all the time. Both cough and pain are much worse after eating evening meal. Identifies pain along the length of throat, a burning in her chest, and reports that her mouth tastes sour along with the presence of excessive saliva in her mouth. Throat lozenges exacerbate the pain but alleviate the bitter taste in her mouth. Ice chips provide temporary relief for pain. Patient feels very anxious about pain, reporting heart palpitations and anxiety: father diagnosed with stage II squamous cell esophageal carcinoma 14 months ago. Patient engaged in smoking cessation program nine months ago after a 12-year smoking habit. In addition to HPI, patient reports loss of appetite. No report of nausea, fever chills, diarrhea, swollen joints, unusual muscle aches, headache, double vision, painful urination, or shortness of breath. No identified skin rash. History of peptic ulcer at age 14, responded well to OTC treatment with no recurrence. Occasional problem with heartburn, but patient admits she has not kept track of her own health due to schoolwork, job and father's health problems. Bronchitis complicated by pleurisy last year, responded well to ABX treatment. No history of asthma. No known drug allergies. Patient is second year law student at Collegetown Law. Alcohol: two to four beers a week average.
PE: 98.2 HR 28, RR 16, BP 115/71
Patient alert and well groomed, but clearly agitated, with flushed face but in no acute distress. Eyes clear without jaundice, EOMI intact, PERRLA. No nasal congestion noted. Oral examination reveals sour odor and copious amounts of salivation present along gum line and beneath tongue. Otherwise, oral mucosa intact. Oropharynx red but no inflammation or exudates noted along tonsils or adenoids. Neck soft without masses and non-tender, although patient reports radiating pressure when upon palpation of submaxillary lymph glands with significant pain upon swallowing during exam. Lungs clear to auscultation and percussion. Abdomen soft, nontender upon palpation. Normal bowel sounds present. Patient alert, oriented times three. Cranial nerves intact. Extremities warm, well-perfused without rash or indurations. Patient displays appropriate judgment, insight and recall, but is very anxious her painful throat and her father's poor response to treatment; patient becomes quite tearful and displays signs of depression and anxiety about her father's illness and she is very fearful that her sore throat is the same disease process as her father's.
Impression: 29-year-old woman with possible extraesophageal manifestation of GERD.
Plan: Chest X-ray ordered to rule out lung congestion or esophageal mass. Upon review of X-ray, consider proton pump inhibitor therapy and change of lifestyle to reduce stress and improve digestion, including eating five small meals throughout day and no food or drink more than 3 hours before bedtime.
Over 60 minutes were spent in providing counseling for patient regarding her possible diagnosis and her anxiety regarding her father's illness, her own presenting problem, and recommend that she consider pursuing visits with social worker or psychotherapist regarding her anxiety. Follow up in one week to review patient's response to pump inhibitor therapy and lifestyle changes.
Indicate whether this statement is true or false.
Question 2
The physician's documentation of the face-to-face intraservice time is appropriate and supports counseling and coordination of care.
Cassidy presents to the Collegetown Clinic today for evaluation of throat pain and productive cough.
29-year-old woman is a new patient presenting with worsening daytime cough. Over the past three weeks, cough has become more persistent and hoarse, but cough does not interrupt sleep. Throat burns constantly during day. No identified postnasal drip, although patient rates throat pain at 8/10 all the time. Both cough and pain are much worse after eating evening meal. Identifies pain along the length of throat, a burning in her chest, and reports that her mouth tastes sour along with the presence of excessive saliva in her mouth. Throat lozenges exacerbate the pain but alleviate the bitter taste in her mouth. Ice chips provide temporary relief for pain. Patient feels very anxious about pain, reporting heart palpitations and anxiety: father diagnosed with stage II squamous cell esophageal carcinoma 14 months ago. Patient engaged in smoking cessation program nine months ago after a 12-year smoking habit. In addition to HPI, patient reports loss of appetite. No report of nausea, fever chills, diarrhea, swollen joints, unusual muscle aches, headache, double vision, painful urination, or shortness of breath. No identified skin rash. History of peptic ulcer at age 14, responded well to OTC treatment with no recurrence. Occasional problem with heartburn, but patient admits she has not kept track of her own health due to schoolwork, job and father's health problems. Bronchitis complicated by pleurisy last year, responded well to ABX treatment. No history of asthma. No known drug allergies. Patient is second year law student at Collegetown Law. Alcohol: two to four beers a week average.
PE: 98.2 HR 28, RR 16, BP 115/71
Patient alert and well groomed, but clearly agitated, with flushed face but in no acute distress. Eyes clear without jaundice, EOMI intact, PERRLA. No nasal congestion noted. Oral examination reveals sour odor and copious amounts of salivation present along gum line and beneath tongue. Otherwise, oral mucosa intact. Oropharynx red but no inflammation or exudates noted along tonsils or adenoids. Neck soft without masses and non-tender, although patient reports radiating pressure when upon palpation of submaxillary lymph glands with significant pain upon swallowing during exam. Lungs clear to auscultation and percussion. Abdomen soft, nontender upon palpation. Normal bowel sounds present. Patient alert, oriented times three. Cranial nerves intact. Extremities warm, well-perfused without rash or indurations. Patient displays appropriate judgment, insight and recall, but is very anxious her painful throat and her father's poor response to treatment; patient becomes quite tearful and displays signs of depression and anxiety about her father's illness and she is very fearful that her sore throat is the same disease process as her father's.
Impression: 29-year-old woman with possible extraesophageal manifestation of GERD.
Plan: Chest X-ray ordered to rule out lung congestion or esophageal mass. Upon review of X-ray, consider proton pump inhibitor therapy and change of lifestyle to reduce stress and improve digestion, including eating five small meals throughout day and no food or drink more than 3 hours before bedtime.
Over 60 minutes were spent in providing counseling for patient regarding her possible diagnosis and her anxiety regarding her father's illness, her own presenting problem, and recommend that she consider pursuing visits with social worker or psychotherapist regarding her anxiety. Follow up in one week to review patient's response to pump inhibitor therapy and lifestyle changes.
Indicate whether this statement is true or false.