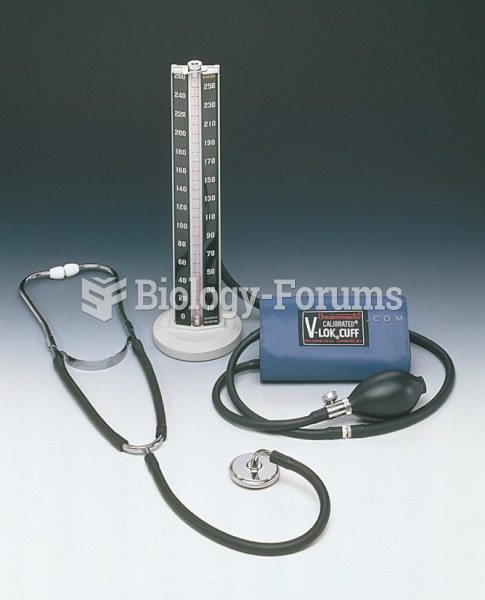
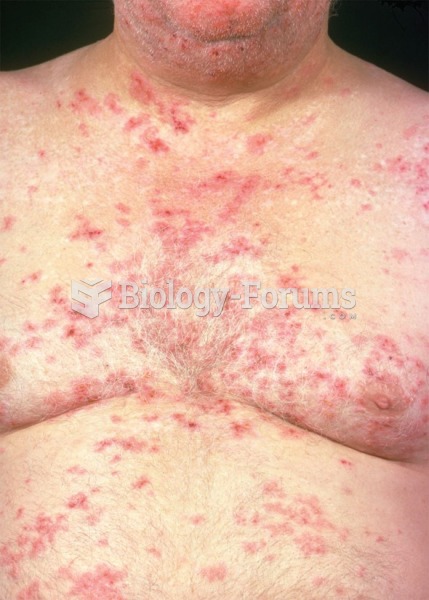
|
|
|
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
A strange skin disease referred to as Morgellons has occurred in the southern United States and in California. Symptoms include slowly healing sores, joint pain, persistent fatigue, and a sensation of things crawling through the skin. Another symptom is strange-looking, threadlike extrusions coming out of the skin.
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
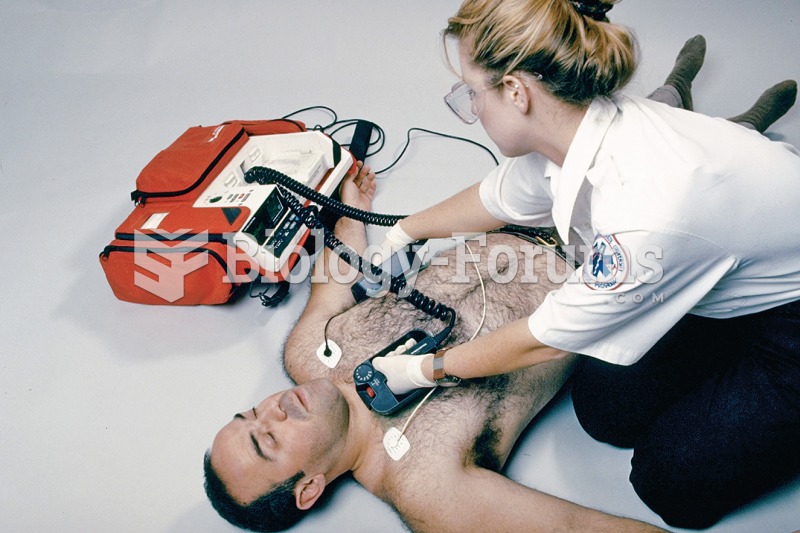 An emergency medical technician positions defibrillator paddles on the chest of a supine male patien
An emergency medical technician positions defibrillator paddles on the chest of a supine male patien
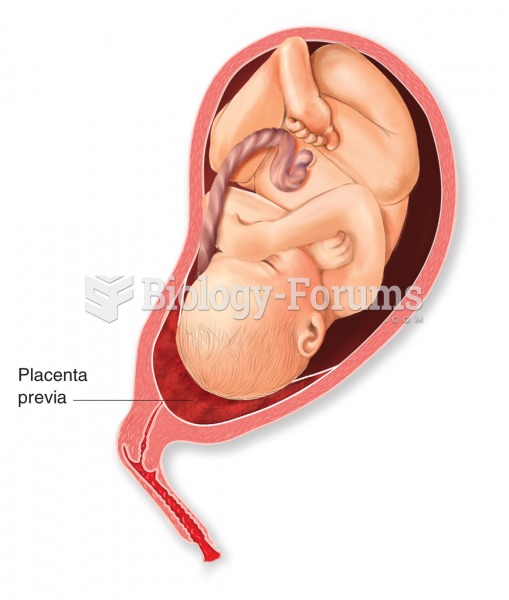 Placenta previa. The condition is caused by the development of the placenta over the cervical canal,
Placenta previa. The condition is caused by the development of the placenta over the cervical canal,