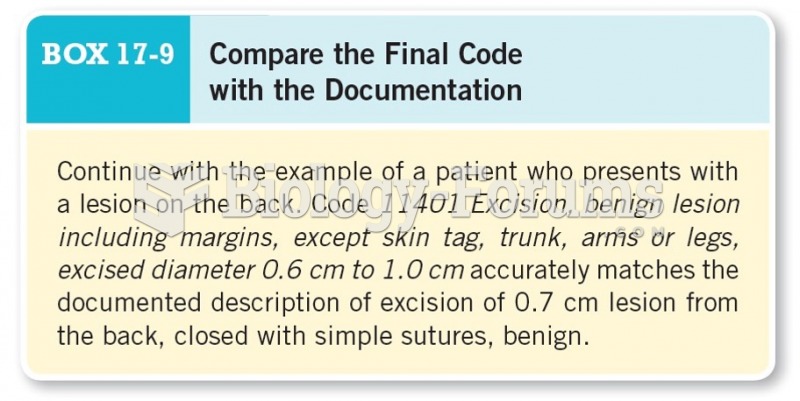
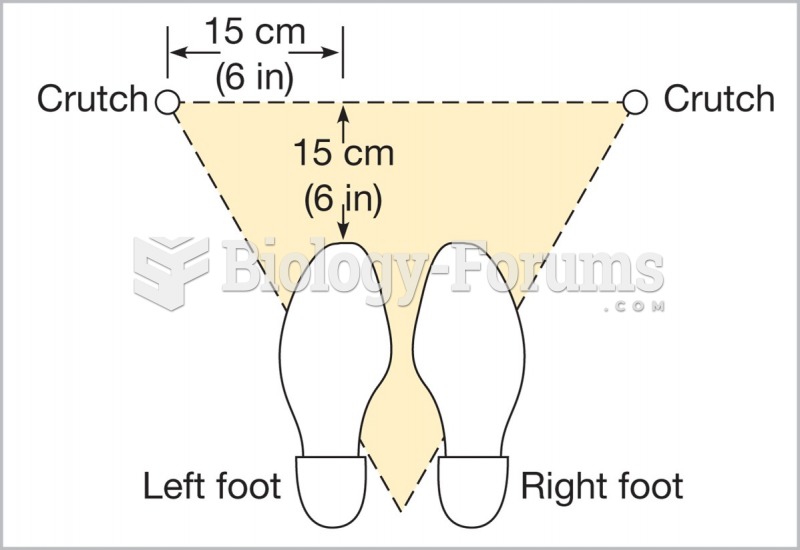
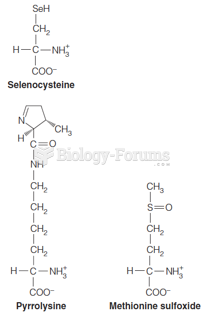
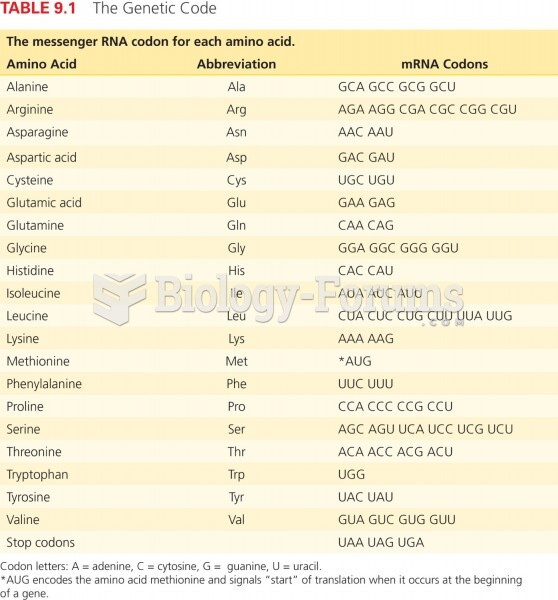
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Did you know?
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
Did you know?
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
Did you know?
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.