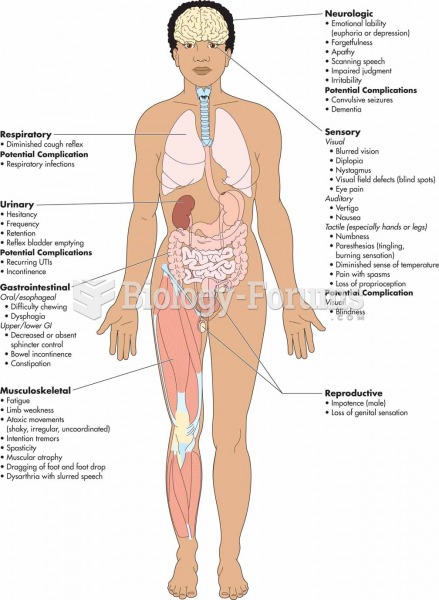
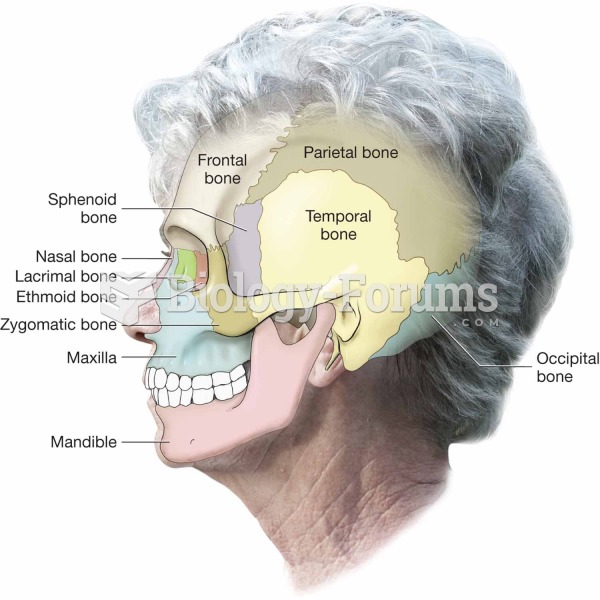
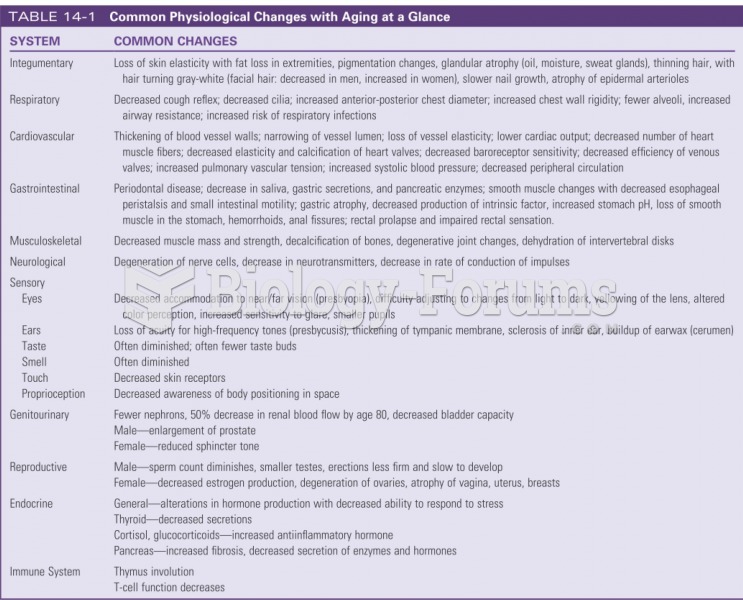
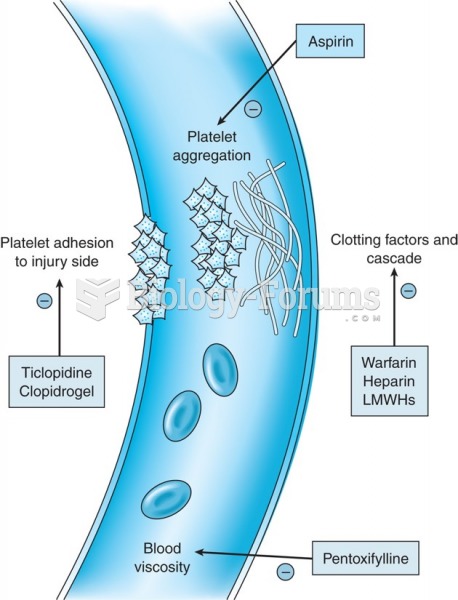
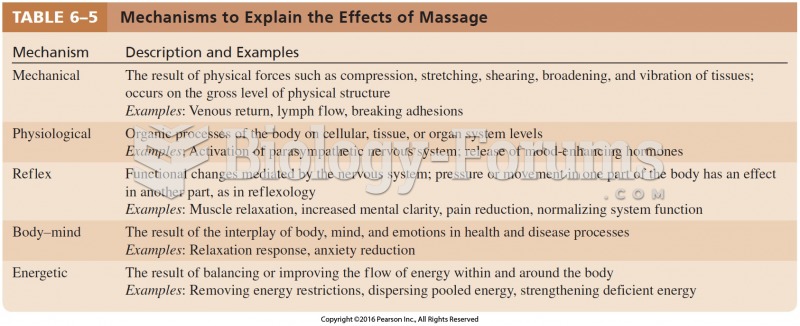
|
|
|
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
The eye muscles are the most active muscles in the whole body. The external muscles that move the eyes are the strongest muscles in the human body for the job they have to do. They are 100 times more powerful than they need to be.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.