|
|
|
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
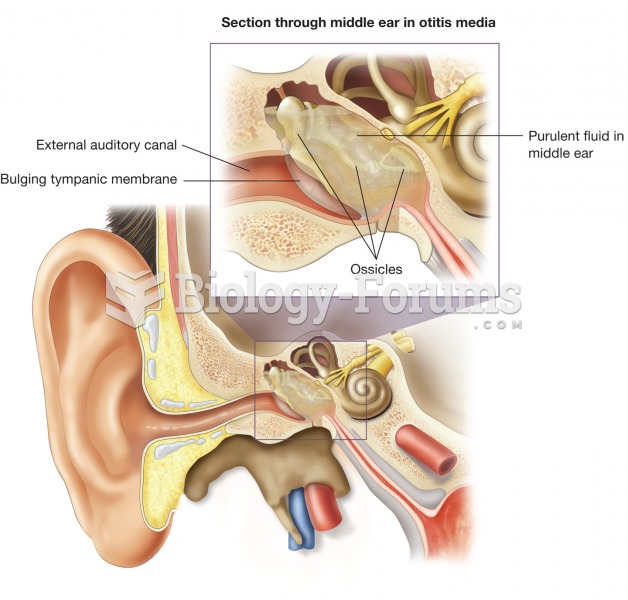 Otitis media. This illustration shows an inflamed tympanic cavity, which is the most common source o
Otitis media. This illustration shows an inflamed tympanic cavity, which is the most common source o
 In 2008, the U.S. economy suffered a gaping wound as several trillion dollars were ripped out of it.
In 2008, the U.S. economy suffered a gaping wound as several trillion dollars were ripped out of it.