This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
Did you know?
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Did you know?
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Did you know?
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Did you know?
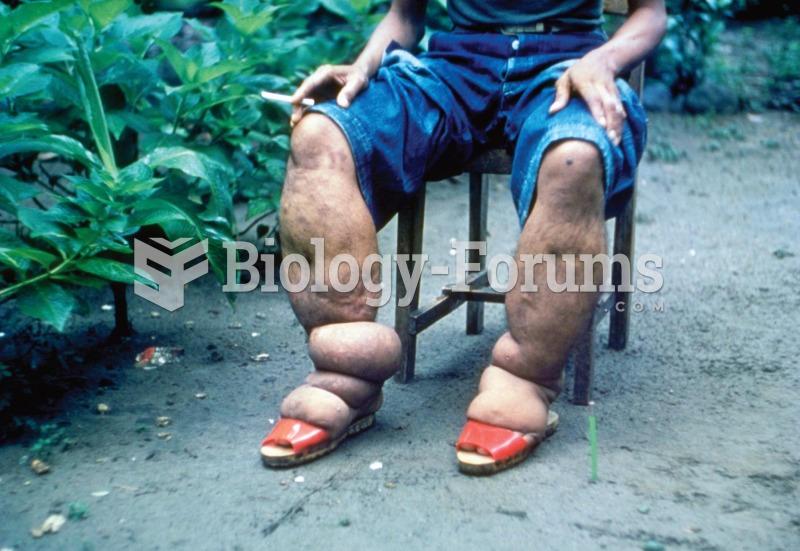
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
 It is important to ask patients what other health care providers they are seeing, such as the dentis
It is important to ask patients what other health care providers they are seeing, such as the dentis
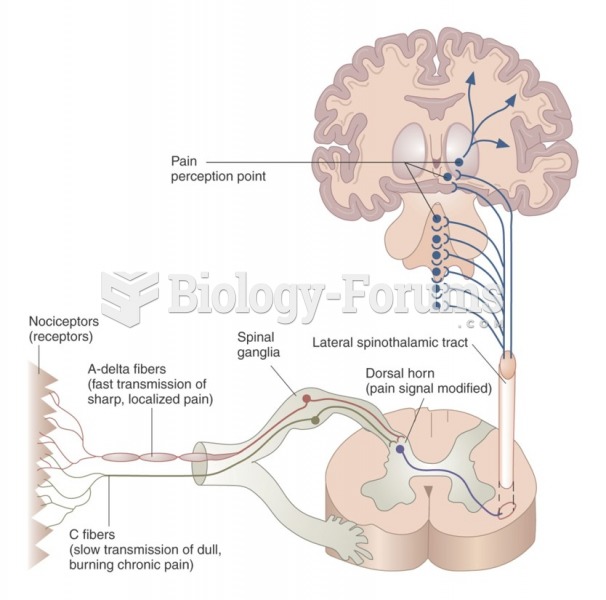
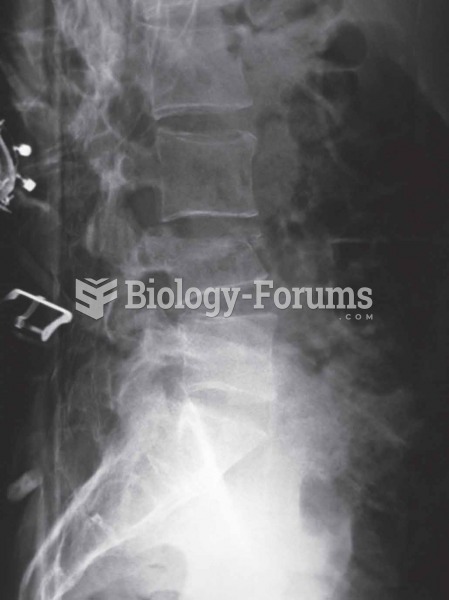 Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia