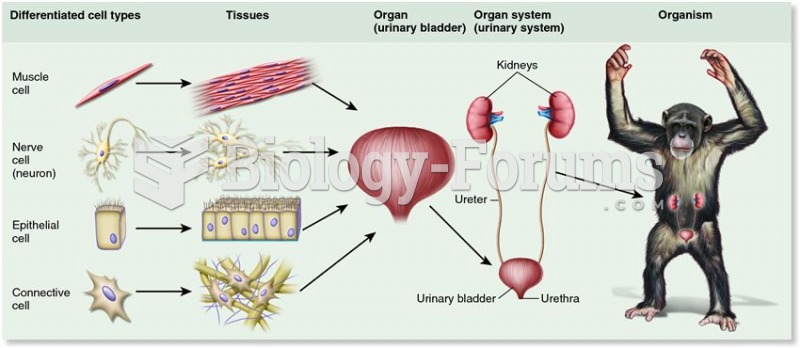
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Did you know?
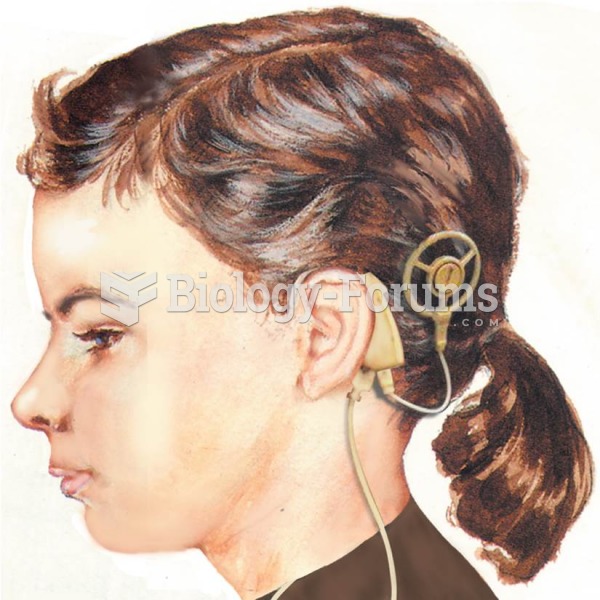
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Did you know?
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.