|
|
|
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Everyone has one nostril that is larger than the other.
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
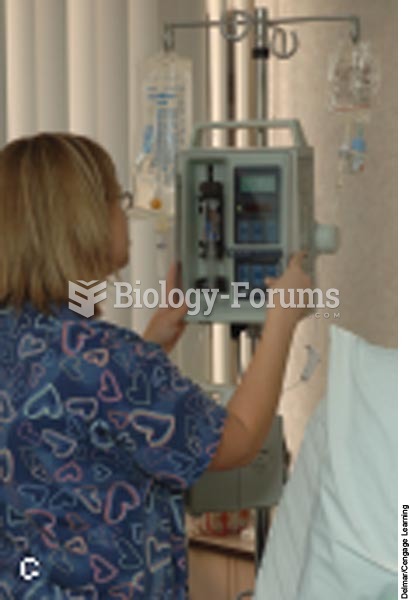
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.