|
|
|
Although not all of the following muscle groups are commonly used, intramuscular injections may be given into the abdominals, biceps, calves, deltoids, gluteals, laterals, pectorals, quadriceps, trapezoids, and triceps.
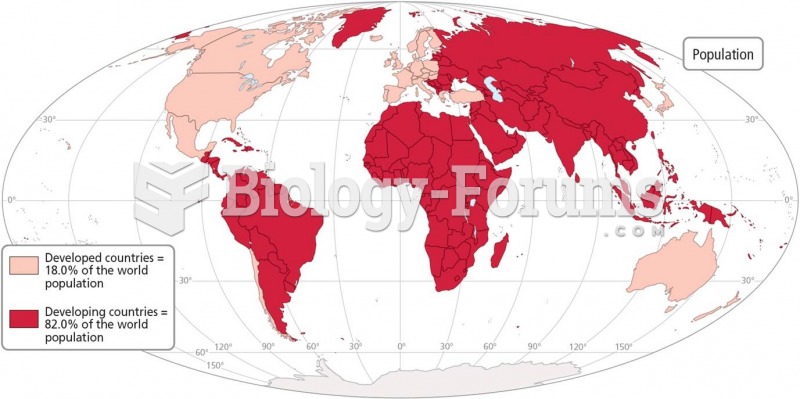
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.