Answer to Question 1
C
Feedback
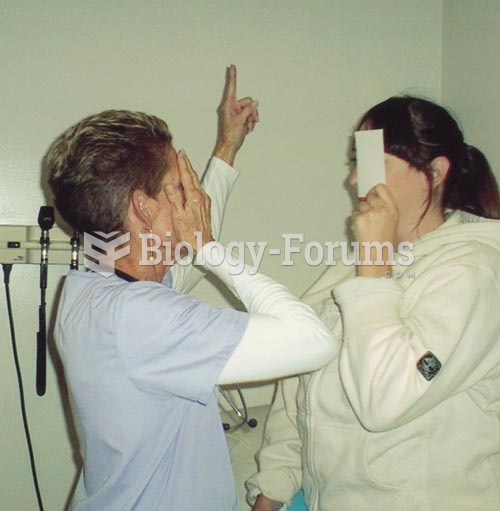
A Fetal position is denoted with a three-letter abbreviation. The first letter indicates
the presenting part in either the right or left side of the maternal pelvis. The
second letter indicates the anatomic presenting part of the fetus. The third letter
stands for the location of the presenting part in relation to the anterior, posterior,
or transverse portion of the maternal pelvis. Palpation of a round, firm fetal part
in the fundal portion of the uterus would be the fetal head, indicating that the
fetus is in a breech position with the sacrum as the presenting part in the
maternal pelvis. Palpation of the fetal spine along the mother's right side denotes
the location of the presenting part in the mother's pelvis. The ability to palpate
the fetal spine indicates that the fetus is anteriorly positioned in the maternal
pelvis. RO/A/ denotes a fetus that is positioned anteriorly in the right side of
the maternal pelvis with the occiput as the presenting part.
B Fetal position is denoted with a three-letter abbreviation. The first letter indicates
the presenting part in either the right or left side of the maternal pelvis. The
second letter indicates the anatomic presenting part of the fetus. The third letter
stands for the location of the presenting part in relation to the anterior, posterior,
or transverse portion of the maternal pelvis. Palpation of a round, firm fetal part
in the fundal portion of the uterus would be the fetal head, indicating that the
fetus is in a breech position with the sacrum as the presenting part in the
maternal pelvis. Palpation of the fetal spine along the mother's right side denotes
the location of the presenting part in the mother's pelvis. The ability to palpate
the fetal spine indicates that the fetus is anteriorly positioned in the maternal
pelvis. LSP describes a fetus that is positioned posteriorly in the left side of the
pelvis with the sacrum as the presenting part.
C Fetal position is denoted with a three-letter abbreviation. The first letter indicates
the presenting part in either the right or left side of the maternal pelvis. The
second letter indicates the anatomic presenting part of the fetus. The third letter
stands for the location of the presenting part in relation to the anterior, posterior,
or transverse portion of the maternal pelvis. Palpation of a round, firm fetal part
in the fundal portion of the uterus would be the fetal head, indicating that the
fetus is in a breech position with the sacrum as the presenting part in the
maternal pelvis. Palpation of the fetal spine along the mother's right side denotes
the location of the presenting part in the mother's pelvis. The ability to palpate
the fetal spine indicates that the fetus is anteriorly positioned in the maternal
pelvis. This fetus is positioned anteriorly in the right side of the maternal
pelvis with the sacrum as the presenting part. RS/A/ is the correct three-letter
abbreviation to indicate this fetal position. Elsevier items and derived items
D Fetal position is denoted with a three-letter abbreviation. The first letter indicates
the presenting part in either the right or left side of the maternal pelvis. The
second letter indicates the anatomic presenting part of the fetus. The third letter
stands for the location of the presenting part in relation to the anterior, posterior,
or transverse portion of the maternal pelvis. Palpation of a round, firm fetal part
in the fundal portion of the uterus would be the fetal head, indicating that the
fetus is in a breech position with the sacrum as the presenting part in the
maternal pelvis. Palpation of the fetal spine along the mother's right side denotes
the location of the presenting part in the mother's pelvis. The ability to palpate
the fetal spine indicates that the fetus is anteriorly positioned in the maternal
pelvis. /A/ fetus that is LOA, would be positioned anteriorly in the left side of
the pelvis with the occiput as the presenting part.
Answer to Question 2
myopia
Myopia (nearsightedness) occurs in early adolescence, between the ages of 11 and 13 and
is a normal part of adolescent development.