Answer to Question 1
C
Feedback
A The woman's race is not a factor for a case of negligence.
B The infant's gender is not a factor for a case of negligence.
C Not meeting the standards of care is a legitimate factor for a case of negligence.
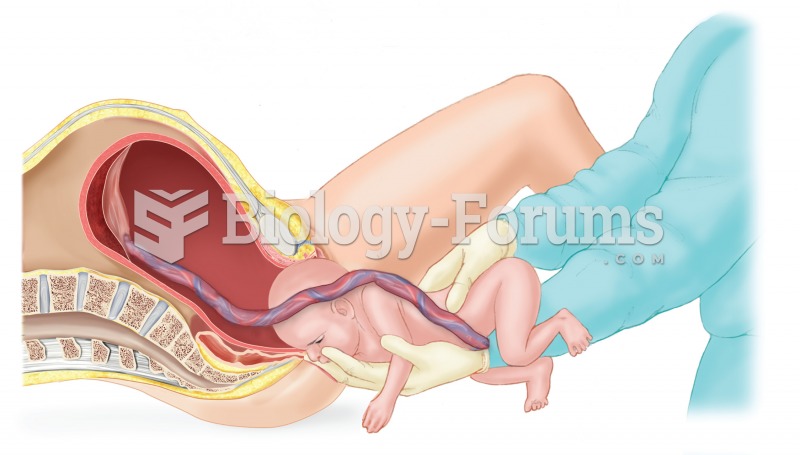
D Although fetal monitoring is the standard of care, the woman has the right to refuse treatment. This refusal is not a case for negligence, but informed consent should be properly obtained, and the woman should sign an against medical ad-vice form for refusal of any treatment that is within the standard of care.
Answer to Question 2
1; 3; 5
Rationale:
1. During implantation, the trophoblast attaches itself to the surface of the endometrium, and between 7 and 10 days, the zona pellucida disappears and the blastocyst implants itself in the thickened uterine lining. The cells of the trophoblast grow down into the thickened lining forming the chorionic villi. The most frequent site of attachment is not the lower part of the anterior wall, but rather the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. The lining of the uterus thickens, rather than thins, below the implanted blastocyst.
2. During implantation, the trophoblast attaches itself to the surface of the endometrium, and between 7 and 10 days, the zona pellucida disappears and the blastocyst implants itself in the thickened uterine lining. The cells of the trophoblast grow down into the thickened lining forming the chorionic villi. The most frequent site of attachment is not the lower part of the anterior wall, but rather the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. The lining of the uterus thickens, rather than thins, below the implanted blastocyst.
3. During implantation, the trophoblast attaches itself to the surface of the endometrium, and between 7 and 10 days, the zona pellucida disappears and the blastocyst implants itself in the thickened uterine lining. The cells of the trophoblast grow down into the thickened lining forming the chorionic villi. The most frequent site of attachment is not the lower part of the anterior wall, but rather the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. The lining of the uterus thickens, rather than thins, below the implanted blastocyst.
4. During implantation, the trophoblast attaches itself to the surface of the endometrium, and between 7 and 10 days, the zona pellucida disappears and the blastocyst implants itself in the thickened uterine lining. The cells of the trophoblast grow down into the thickened lining forming the chorionic villi. The most frequent site of attachment is not the lower part of the anterior wall, but rather the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. The lining of the uterus thickens, rather than thins, below the implanted blastocyst.
5. During implantation, the trophoblast attaches itself to the surface of the endometrium, and between 7 and 10 days, the zona pellucida disappears and the blastocyst implants itself in the thickened uterine lining. The cells of the trophoblast grow down into the thickened lining forming the chorionic villi. The most frequent site of attachment is not the lower part of the anterior wall, but rather the upper part of the posterior uterine wall. The lining of the uterus thickens, rather than thins, below the implanted blastocyst.
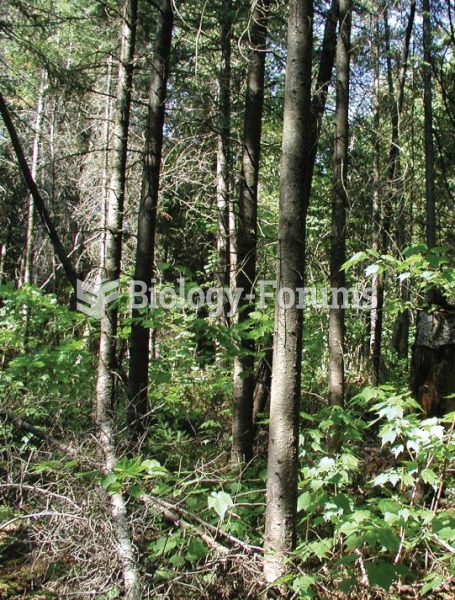 Changes in boreal forest composition along a chronosequence in Quebec. Dates refer to the year of th
Changes in boreal forest composition along a chronosequence in Quebec. Dates refer to the year of th
 In this painting evangelist George Whitefield appears to be cross-eyed. This is no fault of John Wol
In this painting evangelist George Whitefield appears to be cross-eyed. This is no fault of John Wol