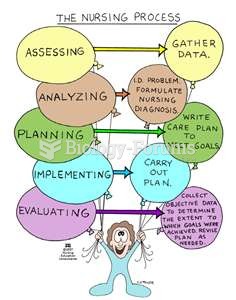
|
|
|
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
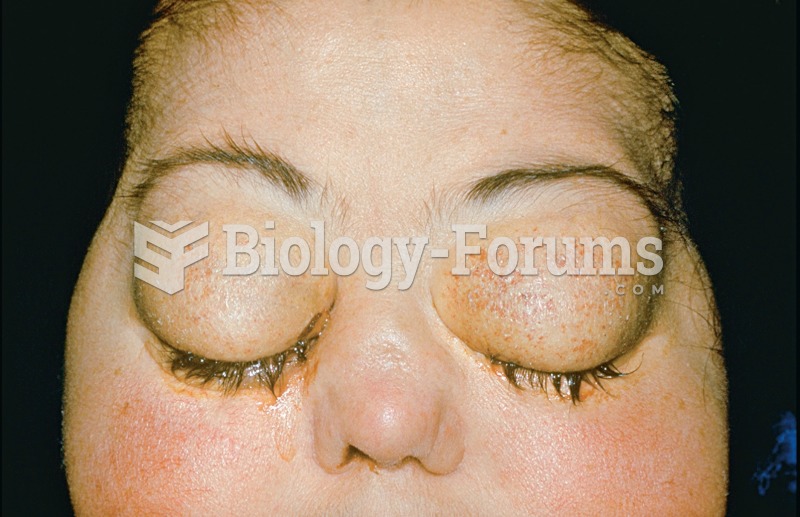
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
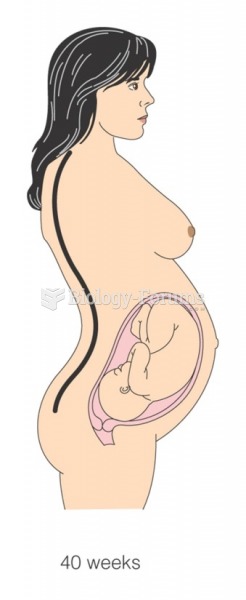
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.