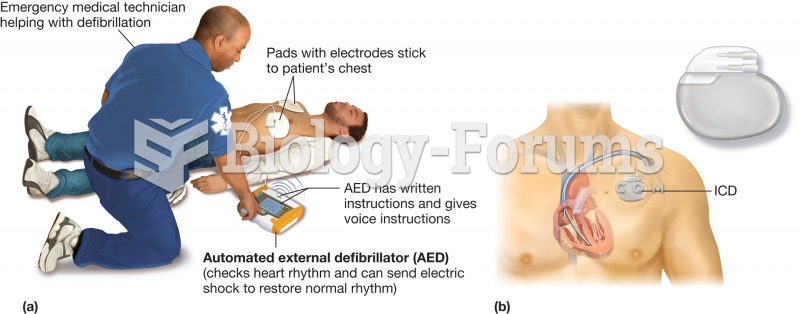
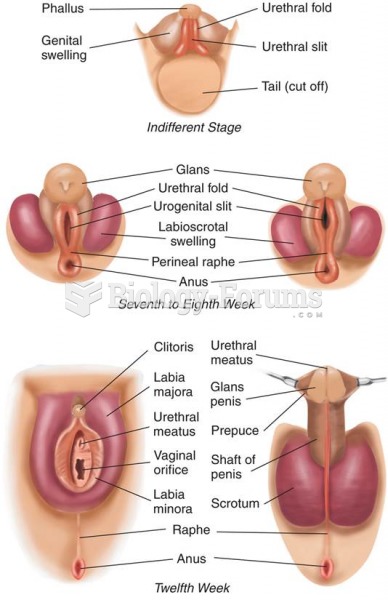
|
|
|
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
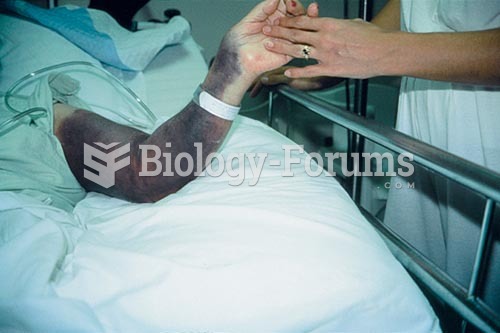 Proper placement and monitoring of an automatic blood pressure cuff will reduce the risk of injury o
Proper placement and monitoring of an automatic blood pressure cuff will reduce the risk of injury o
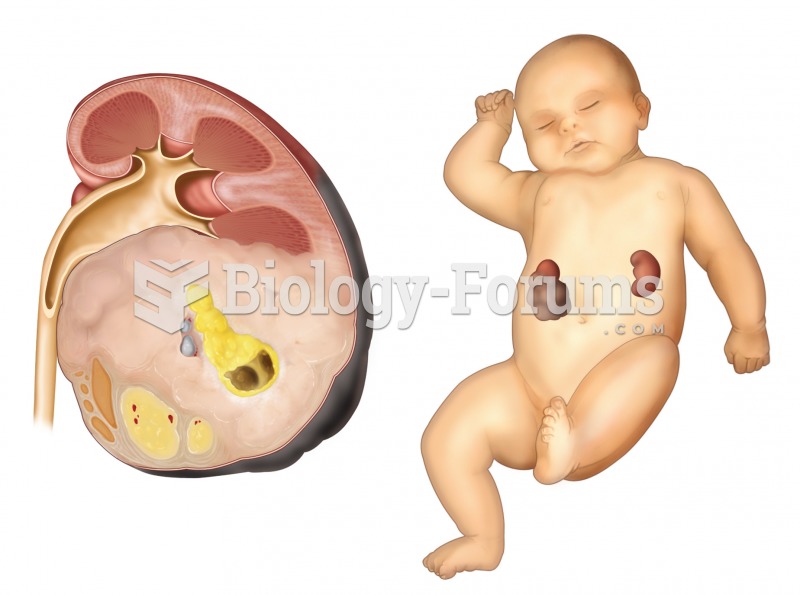 Nephroblastoma. A sectioned kidney reveals the presence of a very large tumor, which arose from feta
Nephroblastoma. A sectioned kidney reveals the presence of a very large tumor, which arose from feta