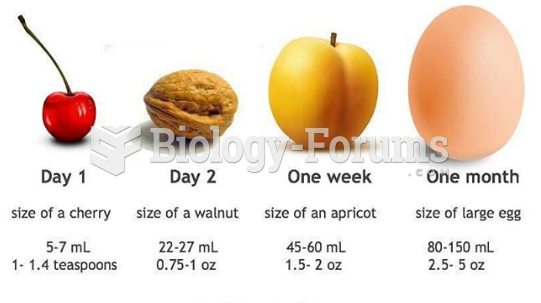
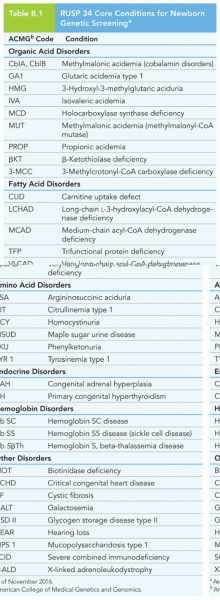
|
|
|
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
Stroke kills people from all ethnic backgrounds, but the people at highest risk for fatal strokes are: black men, black women, Asian men, white men, and white women.
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.