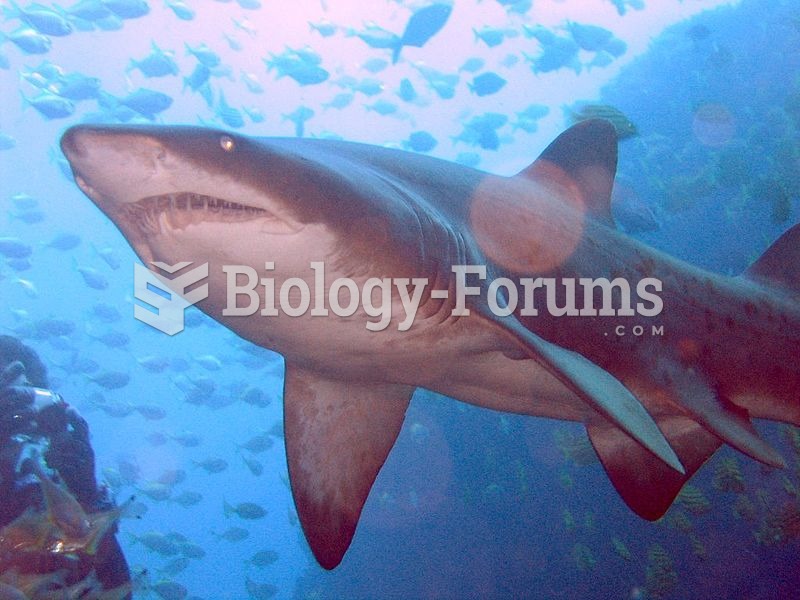
|
|
|
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.