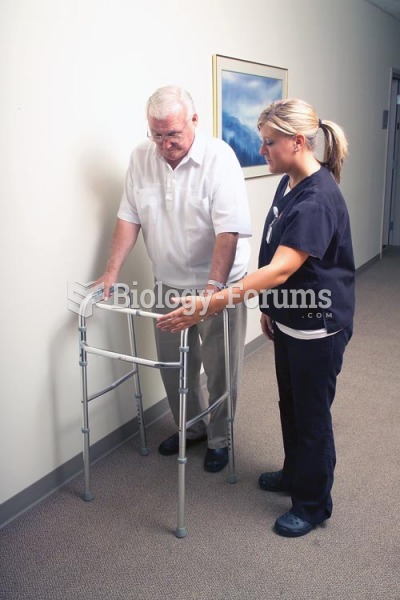
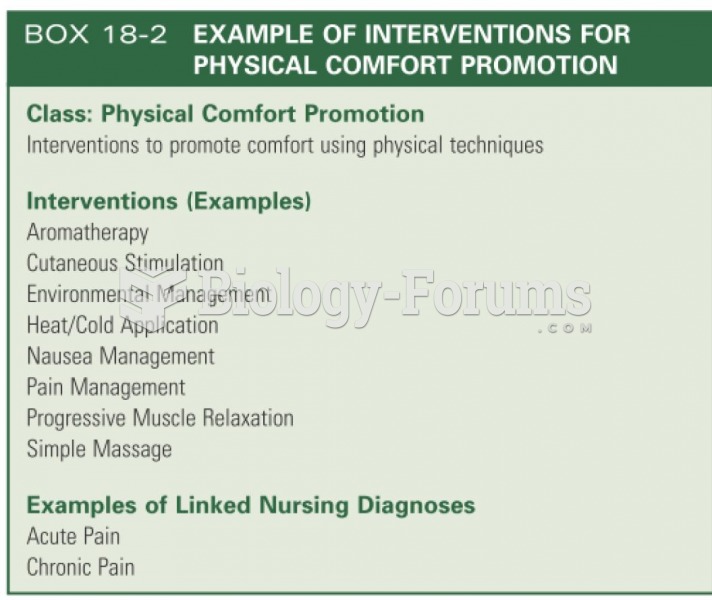
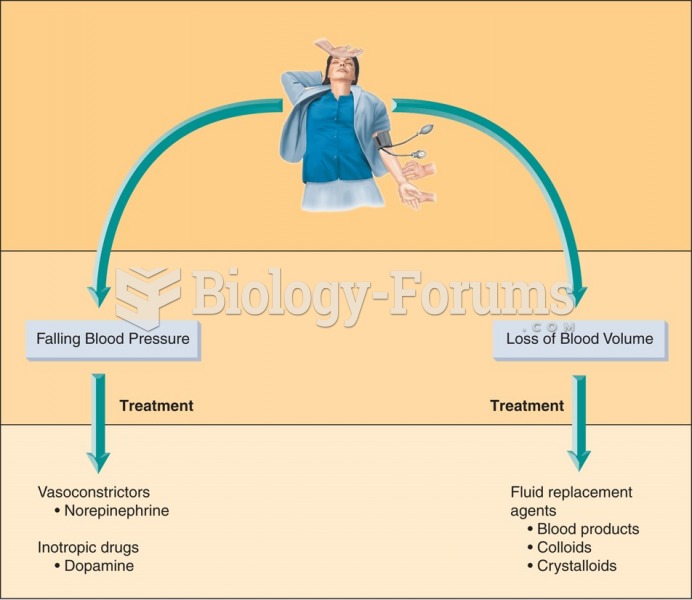
|
|
|
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.