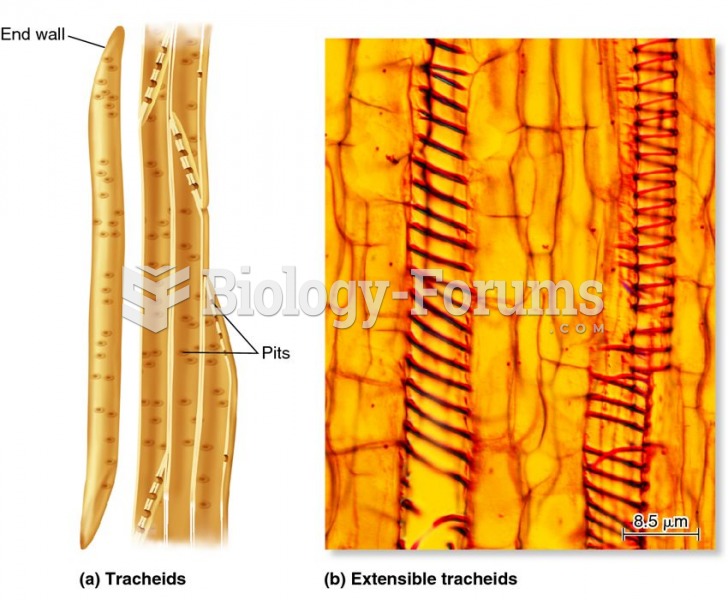
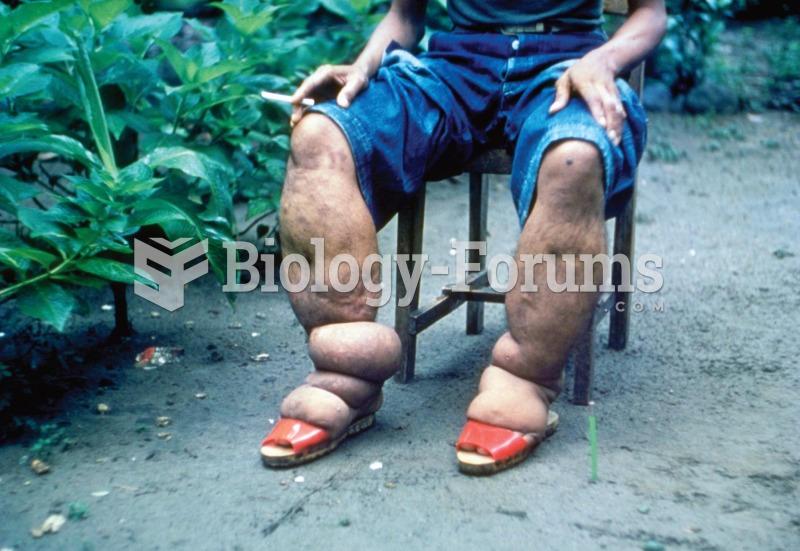
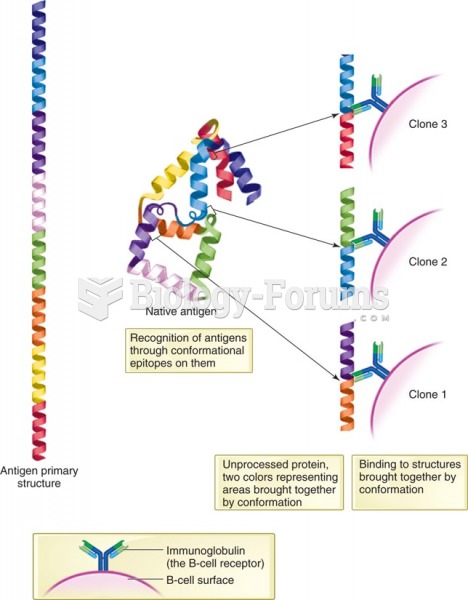
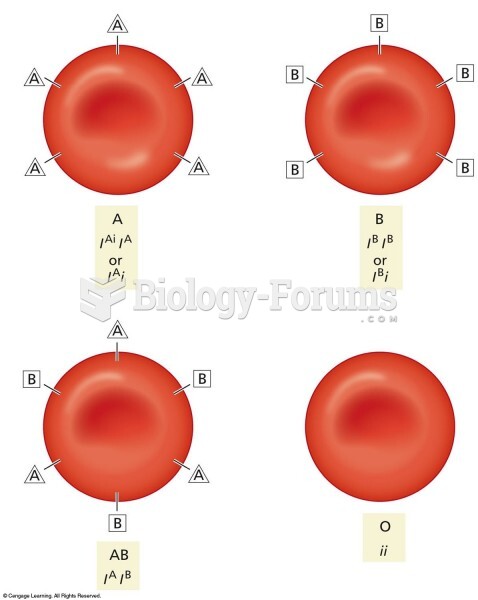
|
|
|
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.