|
|
|
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
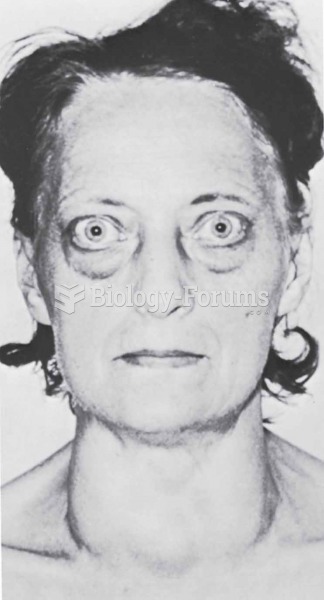
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.