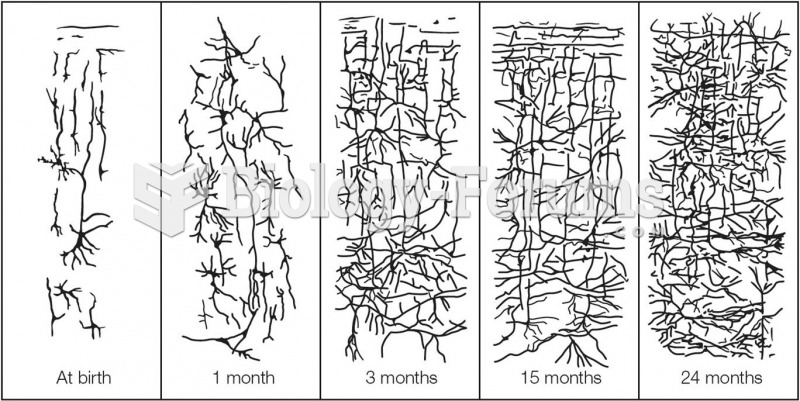
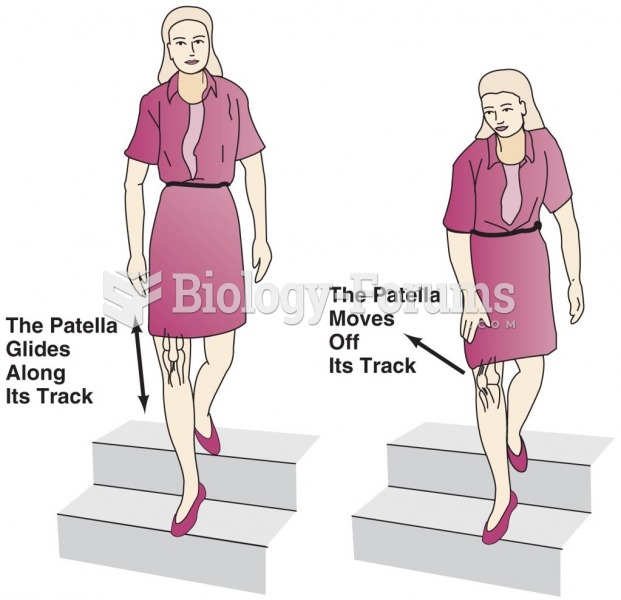
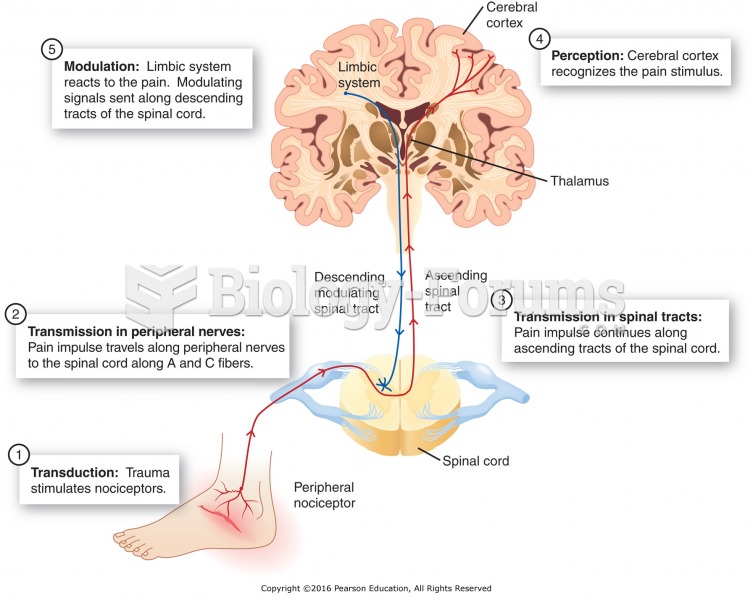
|
|
|
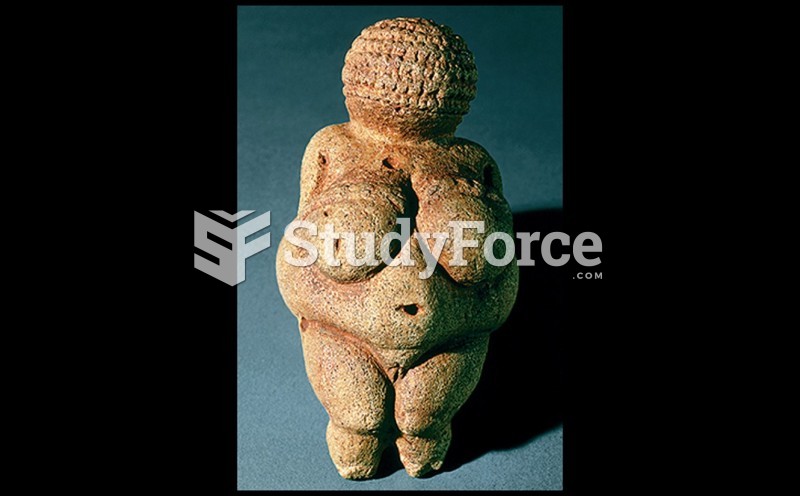
It is believed that the Incas used anesthesia. Evidence supports the theory that shamans chewed cocoa leaves and drilled holes into the heads of patients (letting evil spirits escape), spitting into the wounds they made. The mixture of cocaine, saliva, and resin numbed the site enough to allow hours of drilling.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.